Single-mode and multi-mode fiber patch leads are two of the most commonly used types of fiber optic cables in networking environments. While they both serve the same purpose of transmitting data via light signals, they have significant differences that make them better suited for specific applications. In this blog post, we will take a fresh perspective and provide an in-depth analysis of the differences between single-mode and multi-mode fiber patch leads, and explore how to choose the best one for your needs.
Single-mode vs Multi-mode Fiber Patch Leads: What are the Differences?
| Key Differences | Single-mode Fiber Patch Leads | Multi-mode Fiber Patch Leads |
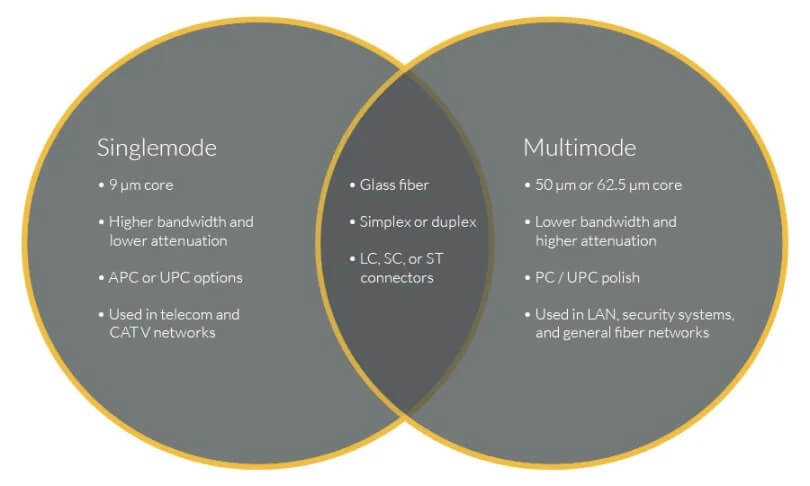
| Core Diameter | Smaller core diameter (typically 9 microns) | Larger core diameter (typically 50 or 62.5 microns) |
| Distance | Ideal for long-distance applications due to lower loss | Better suited for shorter distances |
| Mode Structure | Only allows a single light path to propagate | Allows multiple paths, leading to potential data distortion and loss |
| Wavelength | Uses a single wavelength (1310nm or 1550nm) for transmission | Uses multiple wavelengths (850nm or 1300nm) for transmission |
| Typical Bandwidth | Around 10 Gbps, but this can be increased by using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology | The typical bandwidth of multi-mode fiber patch leads is around 1 Gbps, but this can be increased by using multi-mode fiber patch leads with a larger core diameter, or by using WDM technology |
| Cost | More expensive due to smaller core diameter and advanced technology | Less expensive due to larger core diameter and simpler technology |
| Installation Complexity | More complex due to smaller core diameter and tighter tolerances | Less complex due to larger core diameter and looser tolerances |
| Maintenance Requirements | Requires more precise cleaning and maintenance to maintain performance | Requires less precise cleaning and maintenance to maintain performance |
Single-mode vs Multi-mode Fiber Patch Leads: How to Choose?
Once you grasp the differences between single-mode and multimode fibers, making a choice that suits your project becomes more straightforward. Keeping the following factors in mind will assist you in making your decision.
Distance: How Far Do You Need to Go?
Multimode fiber patch cables excel when it comes to short distances, while single-mode fiber is designed for optimal performance in long-distance signal transmission scenarios. Here are several instances highlighting the distinctions:
- If there is a substantial number of connection points within a building, opting for multimode fiber is the most suitable decision.
- When numerous connection points span a small campus, multimode fiber is the preferred choice.
- For transmitting data from one side of a town to the other, single-mode fiber is the optimal selection.
- When the task involves connecting remote offices situated across different cities, single-mode fiber is the most appropriate option.
Unlike multimode fiber, single-mode fiber isn’t constrained by distance limitations due to its lack of modal dispersion. Single-mode cables can be spliced together to facilitate data transmission over several miles (or even more).
Single mode is particularly well-suited for:
- Undersea applications
- Interconnecting remote offices
- College and university campuses
Bandwidth: How Much Data Do You Need to Send?
The amount of data to be transmitted (the bandwidth required for your application) is another crucial consideration. While multimode fiber can provide significantly higher bandwidth compared to copper systems, single-mode fiber surpasses them all in terms of bandwidth capacity.
Due to its immunity to modal dispersion effects, single-mode fiber boasts virtually unlimited potential in terms of bandwidth.
In contrast, the bandwidth capabilities of multimode fiber are hindered by distortion. As the signaling bandwidth increases, the achievable distance decreases—and conversely—due to modal dispersion. This phenomenon is typically represented as a bandwidth-distance product (MHz∙km). When light rays traverse multiple paths with varying lengths, it leads to disparities in travel distance among the light rays, a phenomenon known as modal dispersion.

Cost: What’s Your Budget for Fiber Optic Optics?
While several factors contribute to determining the cost of a fiber optic network or project, comprehending the differences in material costs is crucial as you weigh the choice between single-mode or multimode fiber.
Traditionally, single-mode cables have represented a budget-friendly choice, but the landscape was different for single-mode electronics (transmitters, receivers, transceivers, etc.). However, with hyperscale data centers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, and Meta adopting single-mode electronics, the costs of these components are being driven down, rendering them more affordable. Consequently, single-mode systems are seeing increased implementation in data center environments.
Conversely, the opposite has been true for multimode: Multimode cables were often seen as expensive, while multimode electronics were relatively more cost-effective, particularly when leveraging LED technology for light generation.
When making the decision between single-mode and multimode fiber, it’s essential to account for these cost factors while also considering functionality. Depending on the specific scenario, enhanced performance might justify a higher expenditure.
Future Upgrades: Are You Planning Ahead for Your Investment?
As you strategize your fiber network, it’s essential to consider its potential requirements in the future. Are there plans for expanding to additional locations? Do you anticipate an escalation in bandwidth demands as you introduce high-speed applications that are currently not in use?
Because single-mode and multimode fibers differ in terms of core size, light source, signal, and laser wavelength, they can’t be interchanged or spliced together. Attempting to do so could lead to significant data loss, jeopardizing the proper functioning of your network.
Hence, it’s imperative to factor in future needs. These considerations can guide your decision-making between single-mode and multimode fiber, not only for present demands but also for those that lie ahead.
For instance, if technologies like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data, or medical imaging are on the horizon, opting for single-mode fiber might be the most prudent choice to ensure compatibility with these advancements down the line.
Summary
At Bonelinks, we pride ourselves on delivering exceptional, personalized technical phone support to our customers. Reach out to our knowledgeable fiber optic team for expert guidance in selecting the perfect fiber optic products to ensure the success of your project.




