As the 5G industry continues to evolve, the demand for efficient communication networks has become a pressing concern for telecom operators. Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN) technology integrates the technical strengths of both PTN (Packet Transport Network) and OTN (Optical Transport Network), catering to a diverse range of market needs and networking applications.
What is POTN?
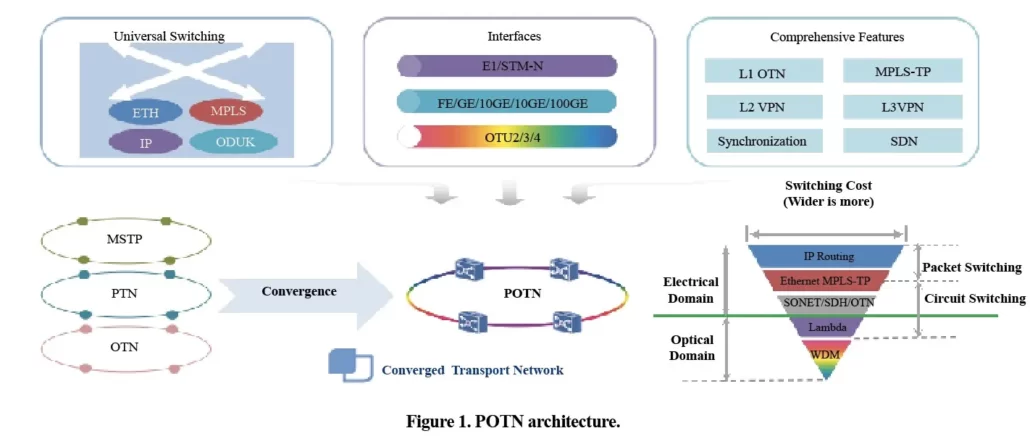
Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN) is a comprehensive network technology that seamlessly combines both packet transport and optical transport technologies. It leverages the strengths of Packet Transport Network (PTN), which establishes a layer between IP services and the underlying optical transmission medium to handle bursty and statistically managed packet traffic, and Optical Transport Network (OTN), which is responsible for the transmission, multiplexing, routing, and monitoring of service signals in the optical domain while ensuring performance and survivability metrics.
Packet Optical Networking Platforms (PONPs) powered by POTN empower service providers and critical optical network operators to deliver TDM-equivalent Ethernet services and build robust infrastructure for various applications. These applications include critical services, wholesale and residential broadband, mobile backhaul, data center interconnect, and enterprise services delivery. POTN is built on a unified packet switching platform, enabling it to support both Layer 2 switching (Ethernet/MPLS) and Layer 1 switching (OTN/SDH). This flexibility allows POTN functions to be adapted and expanded to suit different application and network deployment scenarios.
Challenges Faced by Legacy Networks
The rise of 4G, Ethernet private lines, and home broadband services has ushered in the era of big data, presenting network operators with the following hurdles:
- Bandwidth Deficiency: The demand for bandwidth has surged, with 4G and VIP customer lines requiring hundreds to thousands of megabytes per second. Existing network layers in developed cities struggle to meet these big data era requirements, necessitating urgent network upgrades.
- Network Layer Optimization: Current packet + OTN architecture falls short in terms of rapid service deployment, network protection, and efficient operations and maintenance (O&M). As a result, the industry is shifting focus towards Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN) solutions to simplify network layers and develop converged products.
- Resource Shortage: Extending the traditional packet + OTN architecture to lower layers has brought about issues like high costs, extensive equipment room requirements, rapid resource consumption, and complex service scheduling. POTN addresses these challenges by streamlining network layers and optimizing resources, particularly in addressing the fiber resource shortage through a combination of packet and OTN technologies.
In response to these challenges, POTN has emerged as a pivotal solution for enhancing legacy networks in the face of escalating bandwidth demands, network layer complexities, and resource constraints.
Advantages of Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN)
Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN) presents a host of advantages, rendering it an appealing choice for organizations. Here are the key reasons why businesses opt for POTN:
- Convergence: POTN seamlessly integrates the merits of both packet switching and optical transport technologies, resulting in a unified network infrastructure. This convergence enables the efficient conveyance of both traditional circuit-switched traffic and packet-based data over the same network.
- Flexibility: POTN exhibits remarkable flexibility in terms of accommodating diverse service types, spanning voice, data, and video. This adaptability makes it suitable for a wide array of applications and varying customer demands.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Leveraging its packet switching capabilities, POTN excels in utilizing network bandwidth efficiently. It dynamically allocates resources based on demand, thereby optimizing network utilization and ensuring the efficient utilization of available resources.
- Scalability: POTN is exceptionally scalable, allowing network operators to expand their network capacity seamlessly as traffic demands grow. It offers the flexibility to introduce new services and accommodate future growth without causing significant disruptions to the existing network.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By harnessing the synergy between packet switching technology and optical transport, POTN delivers cost-effective solutions for network operators. It contributes to reducing operational costs, streamlining network management, and facilitating the consolidation of multiple services onto a single, efficient network infrastructure.
These advantages collectively position POTN as a compelling choice for organizations seeking an efficient, adaptable, and cost-effective network infrastructure solution to meet their evolving communication requirements.
POTN Network Positioning and Application Scenarios
POTN serves as an all-encompassing network solution, suitable for deployment in the core, aggregation, and access layers of bearer networks. In areas where the aggregation layer requires higher bandwidth and space is limited, POTN is initially deployed in the metropolitan aggregation layer. For cities lacking a metropolitan Optical Transport Network (OTN), it is implemented in the core aggregation layer.
POTN is versatile and adaptable, offering a virtualized transport network solution tailored to the Software-Defined Networking (SDN) era. Its applications cover trunk bearer services, metropolitan mobile backhaul, metropolitan Optical Line Terminal (OLT) uplinks for home broadband, as well as metropolitan private line and network services.
Conclusion
Embracing Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN) offers a multitude of benefits for organizations. By adopting POTN, businesses can harness the full potential of their networks, revolutionize their operations, and propel themselves into an era of swift digital connectivity.