LAN and SAN stand for Local Area Network and Storage Area Network, respectively, and both are the primary storage networking systems in widespread use today.
A LAN is a collection of computers and peripherals that share a wired or wireless communications link to servers located in different geographic areas. A SAN in a network, on the other hand, provides high-speed connectivity and is designed for private networks, allowing seamless interconnection of multiple servers with a variety of shared storage devices.
As such, the two key components used in the computer network counterpart are LAN switches and SAN switches. Although LAN switches and SAN switches are both channels for data communication, they have some differences, so let’s take a closer look below.
1. What Is LAN Switching?
LAN switching is a packet-switching method used for the transmission of packets between computers on a LAN within a local area network. This technique plays a vital role in network design and can significantly improve LAN efficiency and alleviate bandwidth constraints. There are four types of LAN switching:
Multilayer switching MLS;
Layer 4 switching;
Layer 3 switching;
Layer 2 switching.
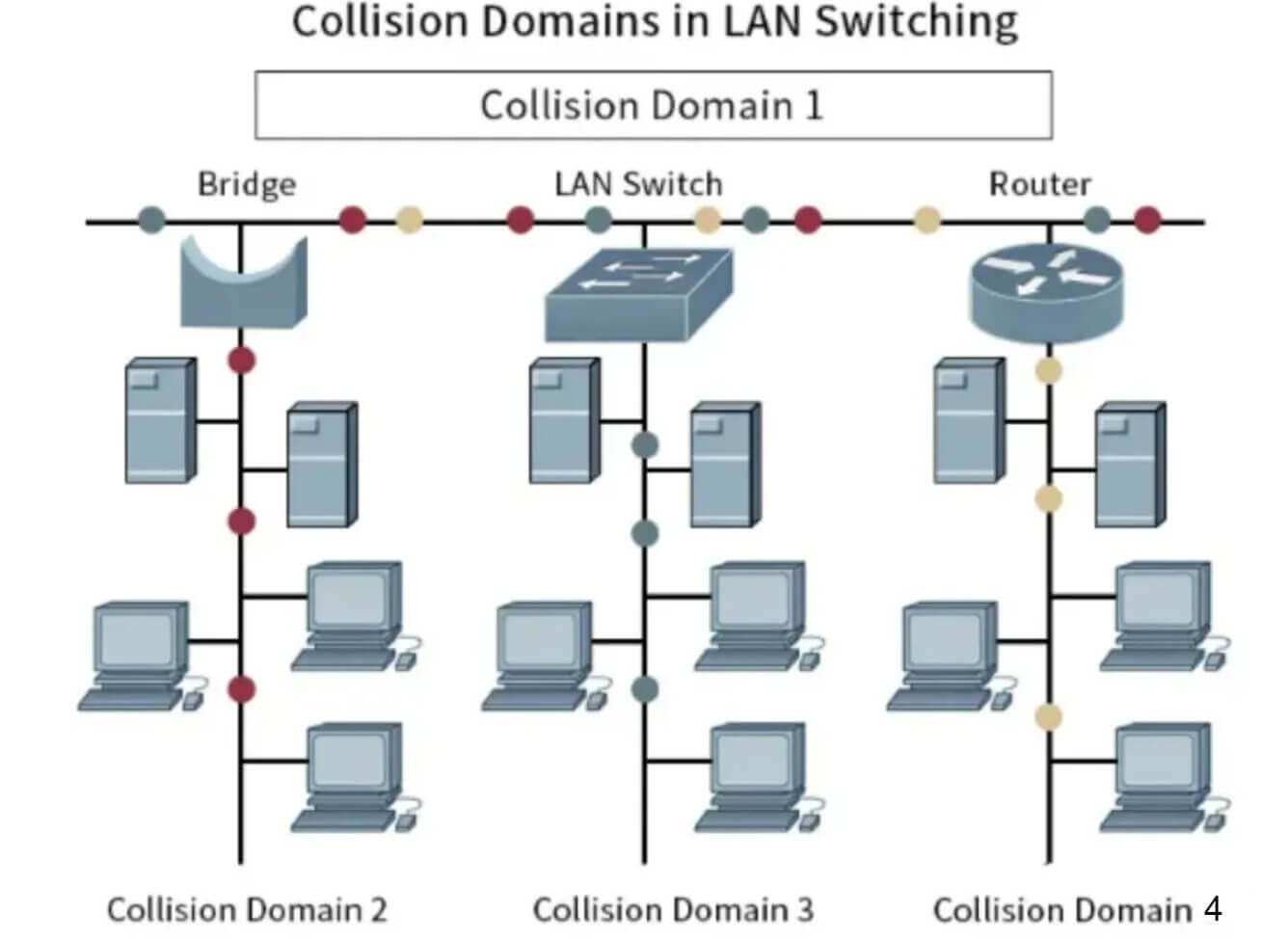
How Does A LAN Switch Work?
A LAN switch is an Ethernet switch that operates on the IP protocol and provides flexible connectivity between senders and receivers through an interconnected network of ports and links. This arrangement allows a large number of end users to share network resources. LAN switches act as packet switches and can handle multiple data transmissions simultaneously. They do this by examining the destination address of each data frame and immediately directing it to a specific port associated with the intended receiving device.
The primary role of a LAN switch is to fulfill the needs of a group of users so that they can collectively access shared resources and communicate seamlessly. By utilizing the capabilities of LAN switches, a large portion of network traffic can be located in relatively compact LAN segments. This segmentation effectively reduces overall LAN congestion, resulting in smoother data transfer and network operation.
2. What Is SAN Switching?
A storage area network SAN switch is a specialized type of switch that creates connections between servers and shared storage pools for the sole purpose of facilitating the transfer of storage-related data.
With SAN switches, it is possible to create large-scale, high-speed storage networks, connecting numerous servers and accessing massive amounts of data, often on the order of petabytes. In their basic operation, SAN switches effectively coordinate traffic between servers and storage devices by inspecting packets and directing them to predetermined endpoints. Over time, network area storage switches have evolved to incorporate advanced features such as path redundancy, network diagnostics, and automatic bandwidth sensing.
How Do Fibre Channel Switches Work?
Fibre Channel switches are key components in a storage area network SAN that help transfer data efficiently between servers and storage devices. The switch operates by creating a high-speed private network designed for data storage and retrieval.
At its core, a Fibre Channel switch relies on specialized hardware and software to manage and direct data traffic. It utilizes the Fibre Channel protocol, a robust and reliable communication protocol tailored for SAN environments. As data is sent from the server to the storage device and vice versa, it is encapsulated in Fibre Channel frames, ensuring data integrity and high-speed transmission.
The SAN switch acts as a traffic policeman to determine the best path for data to travel through the SAN. It examines the source and destination addresses in Fibre Channel frames for efficient routing of packets. This intelligent routing minimizes latency and congestion, ensuring that data reaches its destination quickly and reliably.
Essentially, Fibre Channel switches orchestrate the flow of data in a SAN, optimizing performance and reliability in data-intensive environments.
3. What’s The Difference Between LAN Switch And SAN Switch?
Comparing LAN switches to SAN switches can also be thought of as comparing SAN switches to network switches or comparing Fibre Channel switches to Ethernet switches. Let’s take a look at the main differences between LAN switches and SAN switches.
A. Application Differences
LAN switches were originally designed for token ring and FDDI networks and were later replaced by Ethernet. LAN switches play a vital role in improving the overall efficiency of the LAN and effectively solving the existing bandwidth challenges. LANs can seamlessly connect various devices such as file servers, printers, storage arrays, desktops, etc., and LAN switches can effectively manage the traffic between these different endpoints.
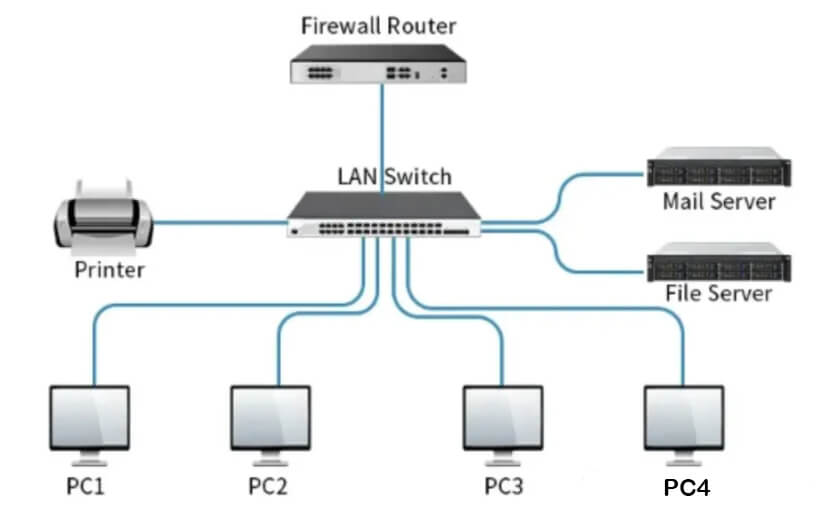
And the SAN switch is designed for high-performance networks to ensure low-latency and lossless data transfer. It is carefully designed to effectively manage heavy transaction loads, especially in high-performance Fibre Channel networks. Whether Ethernet or Fibre Channel, storage area network switches are dedicated and optimized to handle storage traffic.
B. Performance Differences
Typically, LAN switches use copper and fiber optic interfaces and operate over IP-based Ethernet networks. Layer 2 LAN switching offers the benefits of fast data transfer and minimal latency.
It excels in features such as VoIP, QoS and bandwidth reporting. Layer 3 LAN switches offer similar features as routers. As for the Layer 4 LAN Switch, it is an advanced version of the Layer 3 LAN Switch that offers additional applications such as Telnet and FTP.In addition, the LAN Switch supports protocols including but not limited to SNMP, DHCP, Apple Talk, TCP/IP, and IPX.All in all, the LAN Switch is a cost-effective, easy-to-deploy networking solution that is ideally suited for enterprise and advanced networking needs.
SAN switches build on the foundation of iSCSI storage networks, incorporating Fibre Channel and iSCSI technologies. The most important feature is that SAN switches offer superior storage capabilities over LAN switches. Fibre Channel switches can also be Ethernet switches.
Ideally, an Ethernet-based SAN switch would be dedicated to managing storage traffic within an IP storage area network, thus ensuring predictable performance. Also, by interconnecting SAN switches, an extensive SAN network can be formed to connect multiple servers and storage ports.
4. How To Choose The Right Switch?
When considering LAN vs. SAN, the choice of a LAN switch or a SAN switch becomes critical. If your needs include file-sharing protocols such as IPX or AppleTalk, then an IP-based LAN switch is the best choice for storage. Conversely, if you need the switch to support Fibre Channel-based storage, a network area storage switch is recommended.
LAN switches facilitate communication within a LAN by connecting devices within the same network.
Fibre Channel switches, on the other hand, are primarily used to connect storage devices to servers for efficient storage and data retrieval. These switches vary in cost, scalability, topology, security, and storage capacity. The choice between them depends on the specific usage requirements.
LAN switches are inexpensive and easy to configure, while SAN switches are relatively expensive and require more complex configurations.
In conclusion, LAN switches and SAN switches are different types of network switches, each playing a unique role in the network.




