How do fiber optic cables work? How does the large-capacity information optical cable transmit at high speed and long distance?
Overview
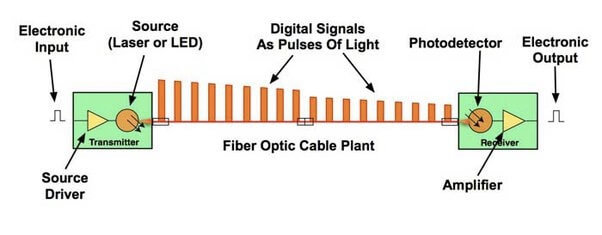
It mainly includes four parts. At the transmitting end, the information to be transmitted (such as voice) is first converted into an electrical signal, and then transmitted to the laser beam by a laser. The intensity of the light varies with the frequency of the electrical signal and is transmitted through the optical fiber. Repeater is used to amplify the signal so that it can be transmitted over a very long distance. At the receiving end, a detector takes the light signal and converts it into an electrical signal, which is processed to restore the original information.
Details
- Transmitter
The most commonly used light sources are Light Emitting Diode(LED) and the semiconductor laser diode. The most commonly used light sources are Light Emitting Diode(LED) and semiconductor laser diode. For transmitting data we convert analog signal to digital signal and pass this digital data to the transmitter which modulates the light stream to enable it to carry the data. Conventionally a pulse of light indicates a “1” and the absence of light indicates “0”. So the transmitter emits a light stream like a digital pulse. - Fiber optic cable
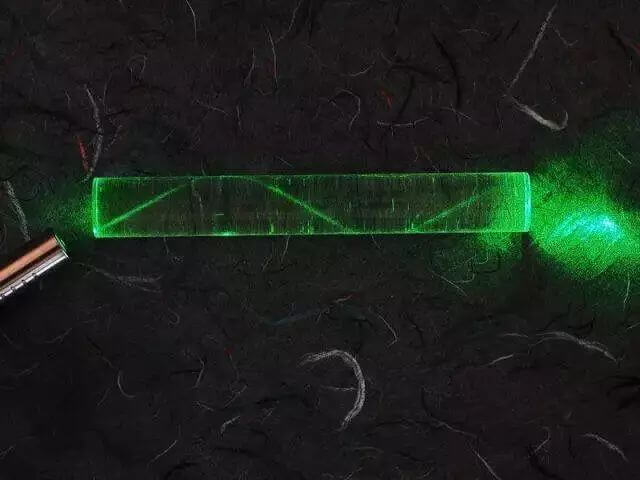
Fiber optic cables consist of optical fibers, which transmit data in the form of light pulses. The optical fibers are too thin and if kept outside are not visible to human eyes. The fibers measure only 1/10 of a strand of hair. Although thin, they can transmit a huge volume of data over them.
Each fiber is distinguished into two parts – the core and the cladding. The core is the part through which the light travels. It is a type of glass cover featuring a low disturbance index. The cladding is a layer that is wrapped around the core and features a deep glass or plastic layer. This layer produces an internal bend. The core and cladding work in combination to produce Total Internal Reflection. It’s one of the things that keeps light inside the pipe.
Total internal reflection occurs at the glass surface and the light cannot escape until it reaches the other end of the fiber. Both visible light and infrared can be used as they can travel long distances in glass with very little being absorbed. A plastic coating prevents scratches on the glass surface which can allow the light to escape from the side of the fiber. Electrical data is converted into a series of light pulses. Light travels down a fiber-optic cable by bouncing repeatedly off the walls. Each tiny photon bounces down the pipe via multiple reflections. The pulses travel down the fiber-optic cable and after traveling down the cable, the light beams emerge at the other end.

- Repeaters
The optical signal is transmitted to the destination through repeated refraction in the optical fiber. After repeated refraction, the optical signal will be scattered or attenuated. Therefore, the optical signal needs to be amplified every 50 kilometers. We generally use repeaters to amplify our signal so that it can be transmitted to a very long distance and also without any distortions. - Receivers
At the receiving point, the detector converts the pulses of light into equivalent electrical pulses. Photodetector is the key part of an optical receiver. It converts light into electricity using photodetector effect. In this way, the data can be transmitted as light over great distances.
Summary
The above is an explanation of how fiber optic cables work. Simply sum up, it works via encoded light pulses. The electrical signals are converted to light pulses. These light pulses are transmitted along the fiber cable. At the receiving end, the light pulses are reconverted to electrical signals and sent to the end user.