Fiber optic networks have been transforming the way data is transmitted and received, offering high-speed and reliable communication. With the increasing demand for faster and more efficient networks, FBT splitters have become an essential component in fiber optic systems. In this blog, we will take a deep dive into FBT splitters and how they play a crucial role in the performance of fiber optic networks.
What is an FBT Splitter?
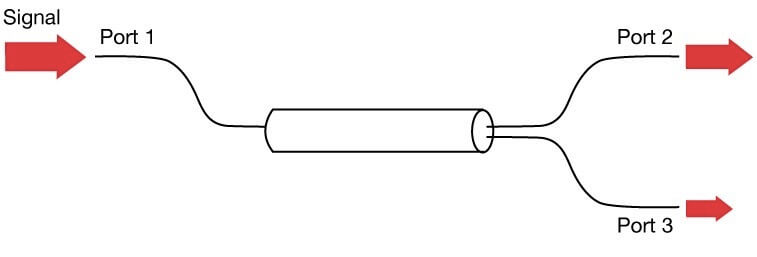
An FBT (Fused Biconic Taper) splitter is a device used to divide or split an optical signal into multiple outputs. It is made up of a single piece of optical fiber that is fused together with a taper and split into two or more fibers. The taper helps to evenly distribute the light from the input fiber to the output fibers, which ensures that the output signals have equal optical power. FBT splitters are used in a variety of applications, including passive optical networks (PONs), data centers, and optical access networks.
How Does an FBT Splitter Work?
FBT splitters work by splitting the light from a single optical fiber into multiple outputs. The light entering the splitter is first collimated and then fed into the taper. The taper is designed to ensure that the light is evenly distributed to the output fibers. The light then travels through the output fibers, which are positioned at different angles, to reach the desired destinations.
FBT Splitter Types
There are several types of FBT splitters, including:
- 1xN FBT splitters: These are used to split an optical signal into multiple outputs, typically 2, 4, 8, 16 or 32. They can be further classified as 1×2, 1×4, 1×8, 1×16, and 1×32 splitters.
- 2xN FBT splitters: These are used to split two optical signals into multiple outputs.
- Custom FBT splitters: These are FBT splitters that are customized to meet specific requirements, such as non-uniform splitting ratios, special connector types, or specific environmental requirements.
- Mini FBT splitters: These are compact FBT splitters that are designed for applications where space is limited.
- WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) FBT splitters: These are FBT splitters that are designed to support WDM systems, where multiple signals of different wavelengths are multiplexed into a single fiber.
In addition to these basic types, FBT splitters can also be classified based on their packaging type, such as rack-mount, wall-mount, or ABS box packaging. The choice of FBT splitter type depends on the specific requirements of the fiber optic network, such as the number of output fibers required, the splitting ratio, and the operating environment.

Features
FBT (Fused Biconical Taper) optical splitters are components used in optical fiber networks to divide an optical signal into multiple paths. The features of FBT optical splitters may include:
- Wavelength Dependence: The ability to work with different wavelengths of light, such as 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
- Low Insertion Loss: A low level of loss when the optical signal passes through the splitter, which helps to maintain the integrity of the signal.
- High Isolation: A high level of isolation between the different output ports of the splitter, which helps to prevent cross-talk and interference between signals.
- Compact Design: A compact and lightweight design, which makes the splitter easy to install and integrate into optical fiber networks.
- High Reliability: High reliability and durability, with the ability to withstand a wide range of environmental conditions.
- Fiber Type Compatibility: Compatibility with different types of optical fiber, such as single-mode and multi-mode fiber.
- Scalability: The ability to scale the splitter to accommodate different network configurations and requirements.
- Low Polarization Dependence Loss (PDL): A low level of PDL, which helps to maintain the quality of the signal and prevent polarization-related errors.
- High Return Loss: A high level of return loss, which helps to minimize reflections and maintain signal quality.
These are some of the common features of FBT optical splitters, but the specific features of a particular implementation may vary depending on the requirements of the network and the specific design of the splitter.
Application
FBT optic splitters are widely used in optical communication systems. They are used to divide an optical signal into multiple outputs while maintaining the integrity of the original signal. Some of the common applications of FBT optic splitters include:
- PON (Passive Optical Network) Systems: FBT splitters are commonly used in PON systems to split the optical signal from a central source to multiple subscribers.
- Optical Distribution Networks (ODN): FBT splitters are used to distribute optical signals in optical distribution networks (ODN) to provide service to multiple users.
- CATV (Cable Television) Networks: FBT splitters are used to distribute optical signals in cable television networks to provide cable television service to multiple users.
- Fiber-optic Sensing: FBT splitters are used in fiber-optic sensing applications to split optical signals for multiple sensing points.
- Optical Test and Measurement: FBT splitters are used in optical test and measurement applications to split the optical signal for multiple test points.
In general, FBT splitters provide a low-cost, reliable and compact solution for optical signal distribution, making them a popular choice for various optical communication systems.

Why are FBT Splitters Important?
FBT splitters play a critical role in fiber optic networks as they help to distribute optical signals evenly. This helps to ensure that the network operates at its maximum capacity and provides a high-quality signal to all connected devices. Additionally, FBT splitters help to reduce the amount of optical loss in the network, which improves the overall signal quality.
FBT splitters are also important in PON networks, where they are used to split the optical signal from a single fiber to multiple subscribers. This helps to reduce the cost of deploying a fiber network as only one fiber is needed to reach multiple users.
Another benefit of FBT splitters is their scalability. They can easily be reconfigured to accommodate changing network requirements, which makes them ideal for use in dynamic environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FBT splitters play a critical role in fiber optic networks. They help to distribute optical signals evenly, reduce optical loss, and improve overall signal quality. FBT splitters are also cost-effective and scalable, making them an ideal choice for use in a variety of applications. With the increasing demand for high-speed and reliable networks, FBT splitters are set to become an increasingly important component in the world of fiber optics. Bonelinks specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. FBT splitter is available at Bonelinks. Please contact us if you have any needs.




