Fiber optic fusion splicing is mainly divided into four steps: stripping, cutting, fusion and protection.
Stripping: refers to the fiber optic cable in the fiber optic core stripped out, which includes the outermost plastic layer, the middle of the steel wire, the inner layer of plastic and fiber optic surface color paint layer.
Cutting: refers to the stripped ready to fuse the end face of the fiber with a “cutter” cut flush.
Fusion: refers to the two optical fibers in the “fusion splicing machine” fused together.
Protection: It means that the fiber optic connector part has been fused with heat shrink tube to protect it.
Each step is described in detail below.
1. Preparation of Endfaces
The preparation of fiber optic endface includes several parts of stripping, cleaning and cutting. Qualified fiber endface is necessary for fusion splicing, and the quality of the endface directly affects the quality of fusion splicing.
A. Stripping Of Fiber Optic Coatings
Skillful mastery of flat, stable, fast three words stripping fiber method. “Flat”, that is, hold the fiber to be flat. Left thumb and forefinger pinch the fiber, so that it becomes horizontal, the exposed length of 5cm for it, the remaining fiber in the ring finger, small thumb between the natural bend to increase the strength, to prevent slippage. “Steady”, that is, fiber stripping pliers to hold steady. “Fast”, that is, stripping the fiber to be fast, fiber stripper should be perpendicular to the fiber, the upper direction of the inward tilt at a certain angle, and then use the jaws of the fiber gently stuck, the right hand and then exerted force, along with the optical fiber axial flat push out, the whole process should be natural and smooth, in one fell swoop.
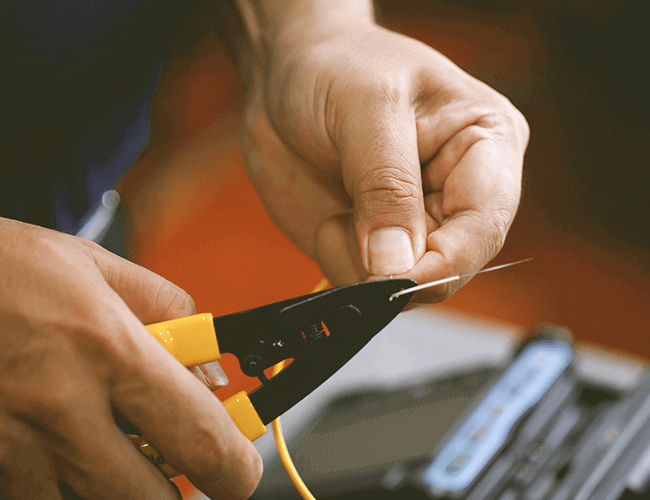

B. Bare Fiber Cleaning
Observe whether the coating layer of the stripped part of the fiber is completely stripped, if there is any residue should be re-stripped. If there is a very small amount of coating layer is not easy to peel off, the cotton ball can be dipped in the appropriate amount of alcohol, while impregnated, and gradually wipe off. A piece of cotton after 2 to 3 times to be replaced in a timely manner, each time to use different parts of the cotton and the level, so as to improve the utilization of cotton, but also to prevent the probe fiber twice the pollution.
C. Bare Fiber Cutting
Cutting is the most critical part of fiber optic endface preparation, precision, excellent cutter is the basis for strict, scientific operation specifications are guaranteed.
Cutting knife selection cutter has manual and electric two kinds. The former is simple to operate, reliable performance, with the operator’s level of improvement, cutting efficiency and quality can be greatly improved, and the requirements of the bare fiber is shorter, but the cutter on the environmental requirements of the temperature difference is higher. The latter cutting quality is higher, suitable for operation in the field under cold conditions, but the operation is more complex, the working speed is constant, and the requirement of bare fiber is longer. Skilled operators at room temperature for rapid fiber optic cable splicing or rescue, the use of manual cutter is appropriate; on the contrary, beginners or in the field under the operation of colder conditions, straight with the electric cutter.
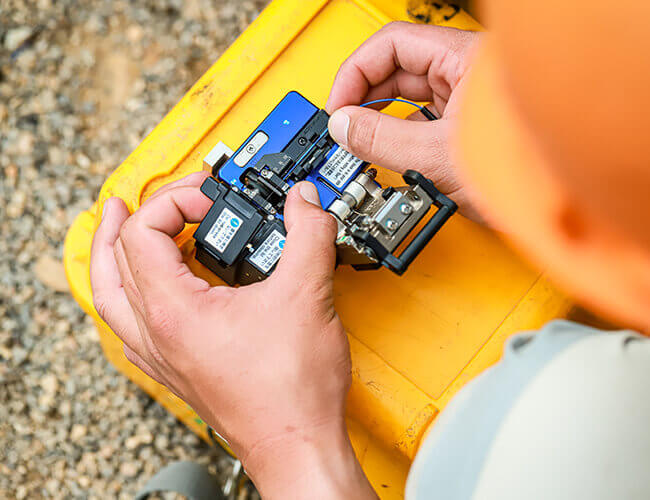

Operation specification operators should be specially trained to master the action and operation specification. First of all, to clean the cutter and adjust the position of the cutter, cutter placement should be smooth, cutting, the action should be natural, smooth, do not heavy, do not rush, to avoid fiber breakage, beveled corners, burrs, cracks and other bad end of the production. In addition, learn to “play the piano”, reasonable distribution and use of their right fingers, so that it corresponds to the specific parts of the cutter, coordinated to improve the cutting speed and quality.
Beware of endface contamination heat shrink tubing should be threaded in before stripping and is strictly prohibited after endface preparation. The time of cleaning, cutting and fusing of bare fiber should be closely connected, not too long an interval, especially the prepared endface should not be placed in the air. When moving, it should be held gently to prevent rubbing with other objects. In the splicing, according to the environment, the cutter “V” shaped groove, pressure plate, knife blade cleaning, to prevent endface contamination.
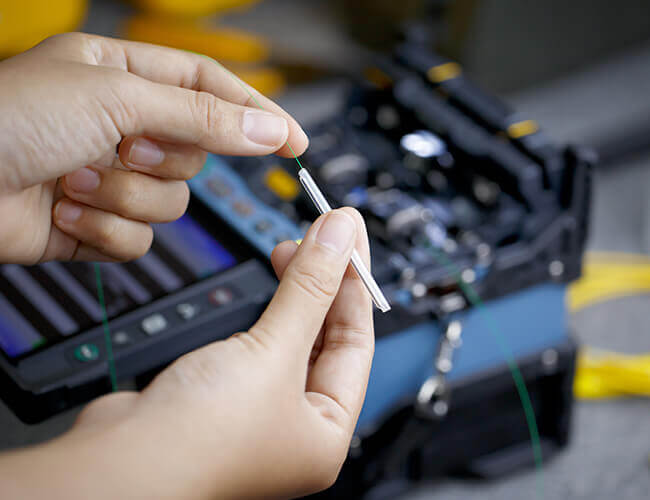

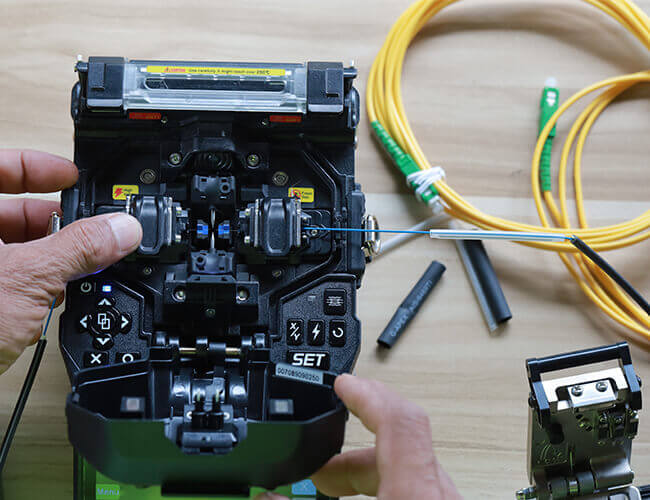
2. Fiber Optic Splicing
Fiber optic fusion splicing is the central part of the splicing work, so high-performance fusion splicing machine and fusion splicing process is very necessary for scientific operation.
A. The Choice Of fusion Splicer
Fusion splicer selection should be based on the requirements of fiber optic cable project with battery capacity and precision of the appropriate fusion splicing equipment.
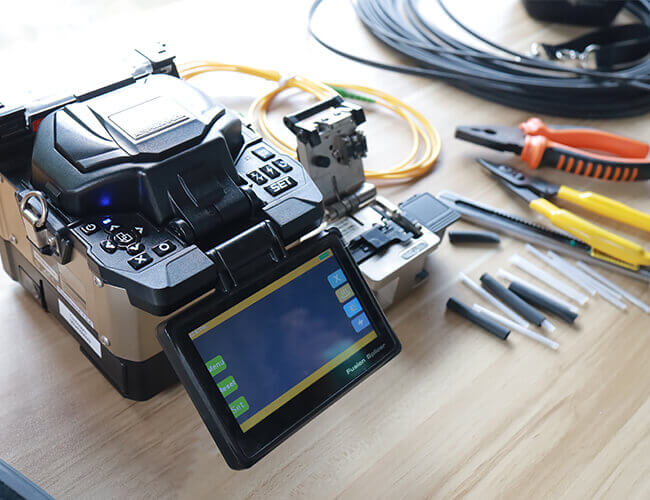
B. Fusion Splicer Parameter Settings
Fusion splicing procedure before splicing according to the material and type of optical fiber, set up the best pre-melting the main fusion current and time and the amount of optical fiber feeding and other key parameters. Fusion splicing process should also be timely clean fusion splicer “V” shaped groove, electrode, objective lens, fusion chamber, etc., at any time to observe the fusion with or without bubbles, too fine, too coarse, false fusion, separation and other undesirable phenomena, pay attention to the results of the OTDR tracking and monitoring, and timely analysis of the causes of the above undesirable phenomena, and to take the appropriate measures to improve the situation. If the phenomenon of false fusion occurs several times, you should check whether the material and type of the two optical fibers to be fused are matched, whether the cutter and the fusion splicer are contaminated by dust, and check the oxidation status of the electrodes, and if there is no problem, you should appropriately increase the fusion current.

3. Fiber Optic Splicing
Coil fiber is a technology, but also an art. The scientific method of coiling fiber can make the fiber layout, additional loss is small, withstand the test of time and harsh environments, can avoid the phenomenon of fiber breakage caused by extrusion.

A. Coil Fiber Rules
Along the loose tube or fiber optic cable branching direction as a unit for the coil fiber, the former applies to all the succession of projects; the latter applies only to the end of the trunk cable, and one into more than one out. Branches are mostly small pairs of fiber optic cables. The rule is that every fusion splicing and heat-shrinking of one or more loose tubes in the fiber, or a sub-technical direction of the optical fiber in the optical fiber, coil fiber once. Advantages: to avoid confusion between the optical fiber loose casing or fiber optic cable between different branches, so that the layout is reasonable, easy to coil, easy to dismantle, more convenient for future maintenance.
B. The Method Of Coling Fiber
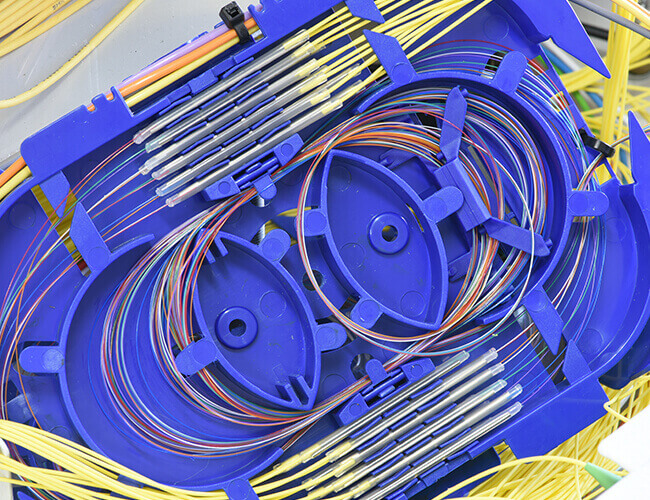
First after the two sides of the middle, that is, the first heat shrinkable casing placed one by one in the fixed slot, and then deal with the remaining fiber on both sides. Advantages: conducive to the protection of fiber optic contacts, to avoid possible damage caused by the coil fiber. In the fiber optic reserved coil space is small, the fiber is not easy to coil and fixed, commonly used this method.
According to the actual situation, adopting a variety of graphics coiled fiber. According to the length of the remaining fiber and the size of the reserved coil space, the natural coiling trend, do not pull hard, should be flexible to use the circle, ellipse, “CC”, “~” a variety of graphic coil fiber (note that the R ≥ 4cm), as far as possible to maximize the use of reserved coil space and effectively reduce additional fiber due to coil space. Reduce the additional loss caused by the coiled fiber.
4. Ensuring The Quality Of Fiber Optic Cable Splicing
Strengthening the monitoring of OTDR is of great significance to ensure the quality of optical fiber splicing and to reduce the additional loss brought about by the coiled fiber and the damage that may be caused to the optical fiber by the sealing box. In the entire splicing work, the OTDR four monitoring procedures must be strictly implemented:
(1) Real-time tracking and monitoring of each fiber core during the splicing process to check the quality of each splicing point;
(2) Each time after the coil fiber, the coil fiber for routine inspection to determine the additional loss brought about by the coil fiber;
(3) Before sealing the splice box, all optical fibers are measured to find out whether there is any leakage and whether there is any extrusion of optical fibers and connectors between optical fiber reservation coils;
(4) After sealing the box, the final test of all optical fibers to check whether the sealing box has any damage to the optical fiber.
In general, fiber optic cable continuity is a meticulous work, especially in the endface preparation, fusion splicing, coil fiber and other links, requiring the operator to carefully observe, careful consideration, operation standardization. In short, in the work, to cultivate a rigorous and meticulous style of work, and diligently summarize and think, in order to improve the practice of operating skills, reduce the splice loss, and comprehensively improve the quality of fiber optic cable splicing.



