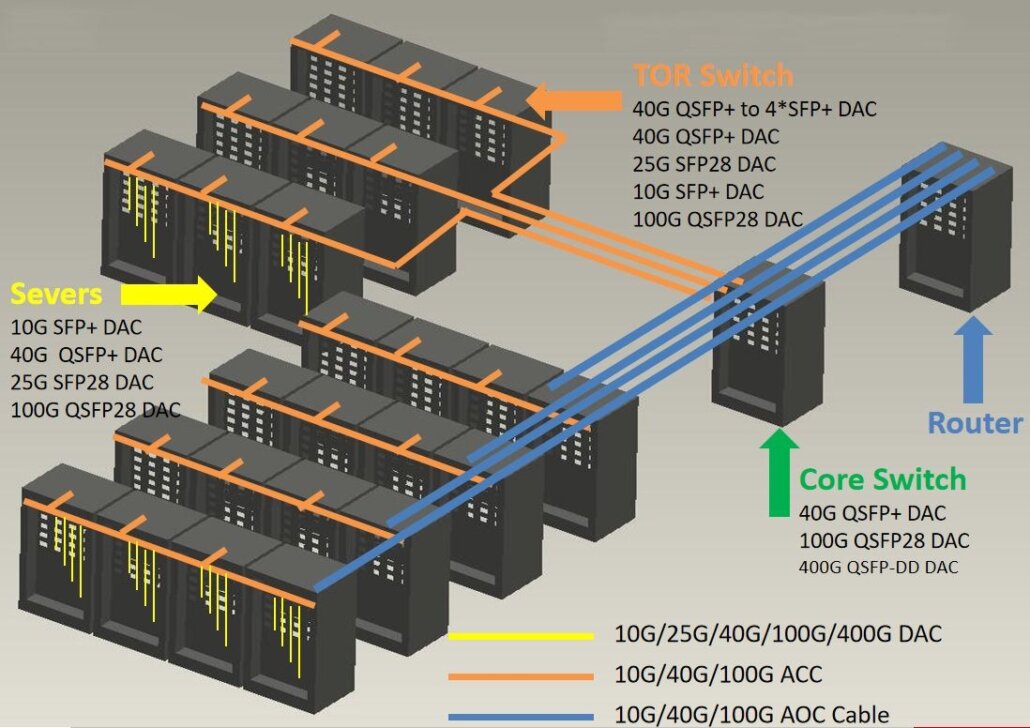
As data centers remain a crucial component of IT infrastructure for businesses of varying scales, addressing cyber security threats and ensuring a resilient infrastructure has led to their increasing significance. Among the prevalent cables in data centers, DAC (Direct Attach Cable) and AOC (Active Optical Cable) play vital roles. To aid IT managers in making informed decisions, it’s important to grasp the distinctions between DAC and AOC cables. This blog will delve into the various types of DAC and AOC cables, help identify the appropriate choice for specific needs, and guide the selection process for the right cable solution.
What is DAC cable?
Direct attach cables (DAC) utilize Twinax copper cables with connectors at both ends to achieve high data-center transmission rates, reaching up to 100G as required.
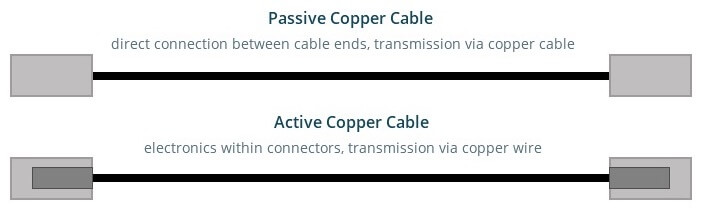
DAC cables are available in two varieties: passive and active, both capable of transmitting over copper. Passive cables omit signal conditioning, minimizing power consumption and production expenses. In active cables, transceivers contain electrical components that amplify signals.
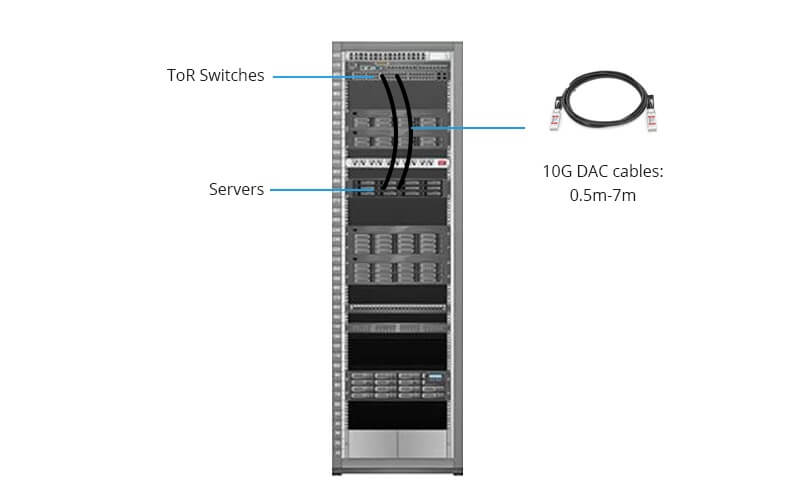
DAC cables excel in short-range scenarios, commonly linking switches, servers, and storage within a rack—typically in data centers. These cables are often pre-terminated in lengths under 10 meters, offering affordability and ease of use compared to other data center cables. Their shorter length contributes to a reduced cost per connection.
What is AOC Cable?
Active optical cables (AOC) are constructed with multimode fiber optics cables featuring SFP connectors on both ends. The ‘active’ in the name signifies the requirement of external power to drive the signal, distinguishing them from passive transmission through fiber optics lines.
AOC cables are predominantly employed in data centers, adept at interconnecting switches, servers, and storage across different racks within the same facility. These cables usually span distances of 100 meters or less, achieving speeds up to 400G over such ranges.
The strength of AOC cables becomes evident when comparing their cost-to-capacity ratio within the common 100-meter range they serve.

DAC vs AOC Cables Comparison, what is the Difference?
Selecting the right cable is a crucial decision in creating a cost-effective and efficient data center infrastructure. Though the choice may not be straightforward, considering key factors can significantly influence your cable selection and its optimal utilization.

Power Consumption
In terms of power consumption, AOC cables typically consume more power compared to DAC cables. AOC cables usually consume around 1-2 watts, whereas active DAC cables consume less than 1 watt, and passive DAC cables have an even lower power consumption of under 0.15 watts. This efficiency in power usage makes DAC cables a more economical choice, reducing operating expenses related to power consumption.
Transmission Distance
AOC cables, utilizing optical fiber technology, can transmit data over longer distances, reaching up to 100 meters. In contrast, DAC cables have shorter link length limits, with passive DAC reaching around 7 meters and active DAC reaching up to 10 meters. Overall, DAC solutions are better suited for short-range transmissions, while AOC solutions are more appropriate for long-range networking scenarios. It’s important to note that the maximum transmission distance for DAC cables varies based on the data rate, decreasing as the data rate increases. For instance, 100G DAC cables may only transmit up to 5 meters.
Cost
DAC cables have a simpler internal structure with fewer components, and copper cables are generally less expensive than fiber cables. Implementing DAC cables in large-scale data centers can result in significant cost savings compared to AOC options. DAC cables are cost-effective for short-range applications. However, for long-range applications, it’s advisable to compare the overall costs of both options.
EMI Immunity
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can disrupt electrical circuits and is generated by external sources. AOC cables, which use optical fibers that do not conduct electric current, are immune to EMI. They are suitable for most environments. On the other hand, due to the conductive nature of copper in DAC cables, they are susceptible to EMI effects. Therefore, the surrounding environment plays a crucial role in avoiding undesirable responses, degradation, or system failures when using DAC cables.
DAC/AOC Working Scenarios
DAC Cable Typical Application
10G SFP+ DAC cables are primarily used for connecting switches and servers within or near the same rack. They serve as effective alternatives for interconnecting Top of Rack (ToR) switches with servers or for stacking 10GbE switches. With a link length of around 7 meters, these DAC cables offer low power consumption, low latency, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for short-range server-to-switch connections.
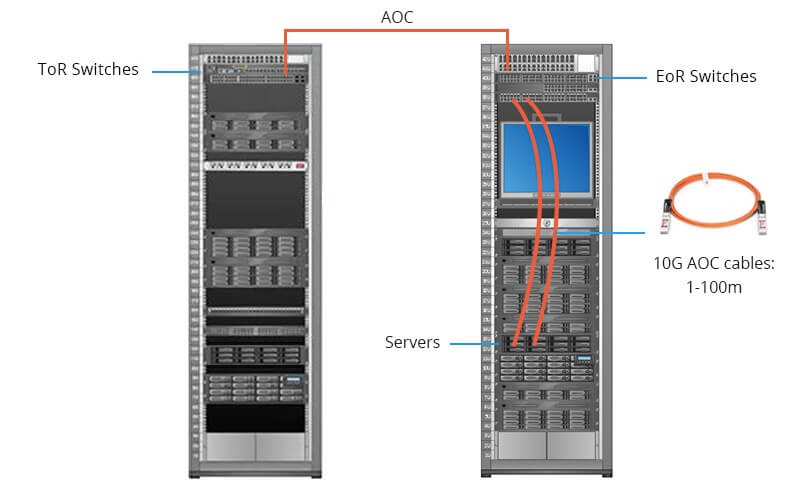
10G SFP+ AOC Cable Typical Application
10G SFP+ AOCs, without strict link length limitations, find common usage in various areas of the data center, such as Top of Rack (ToR), End of Row (EoR), and Middle of Row (MoR). Servers connecting to a ToR Ethernet switch can be equipped with one or two Ethernet connections linked using AOC cables.
Moreover, 10G AOCs play a significant role in different networking segments within the data center, including Spine, Leaf, and Core switching areas. These 10G SFP+ AOCs facilitate interconnections, offering theoretical maximum reaches of up to 100 meters.
How to Choose Between DAC & AOC Cable?
When deciding between DAC and AOC cables for high-performance network connectivity in data centers, consider the following factors:
Application and Distance
Determine the required transmission distance. AOC cables are suitable for longer distances, up to 100 meters, making them ideal for connecting devices across racks or different areas of the data center. DAC cables are better suited for short-haul transmission within the same rack.
Bandwidth and Flexibility
Consider the bandwidth requirements and physical flexibility. AOC cables maintain a consistent diameter regardless of bandwidth, making them more space-efficient and easier to install in tight spaces. DAC cables’ thickness increases with higher bandwidth, which can impact cable management.
Power Consumption
Evaluate power consumption needs. DAC cables have low power consumption, making them energy-efficient options for short distances. AOC cables may require external power but offer longer transmission distances.
Cost-Effectiveness
Both DAC and AOC cables offer cost-effective solutions. DAC cables are generally more affordable and suitable for short-range connections. AOC cables might have higher upfront costs but provide longer reach and immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Environmental Considerations
Assess the data center environment for potential electromagnetic interference. AOC cables are immune to EMI due to their optical nature, while DAC cables are susceptible to EMI.
Installation Ease
AOC cables are small, lightweight, and easy to install, making them well-suited for various setups. DAC cables’ increasing thickness with higher bandwidth can impact installation in tight spaces.
In summary, choose DAC cables for short-distance connections within the same rack, focusing on cost-effectiveness and low power consumption. Opt for AOC cables when longer distances, higher bandwidth, immunity to EMI, and ease of installation are priorities.
Conclusion
DAC and AOC cables are vital elements in data center cabling. Understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right cable and optimizing costs. DAC cables are cost-effective for distances under 5 meters, while AOC cables offer superior performance and pricing for distances beyond 5 meters. Remember, the decision-making process isn’t always simple. Considering key factors will guide your cable choice and usage.
Explore bonelinks.com for a wide range of exceptional DACs and AOCs. Feel free to contact us for more options and information!