The Internet is crucial in today’s world, with Ethernet cables serving as vital connections. However, not all Ethernet cables are alike; various versions are suited for different situations. This article offers a thorough comparison of Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, Cat7a and Cat 8 Ethernet cables to help you make informed choices about your connectivity requirements.
The history lesson reveals a distinct trend: network cables consistently aimed to enhance speed and operational range.

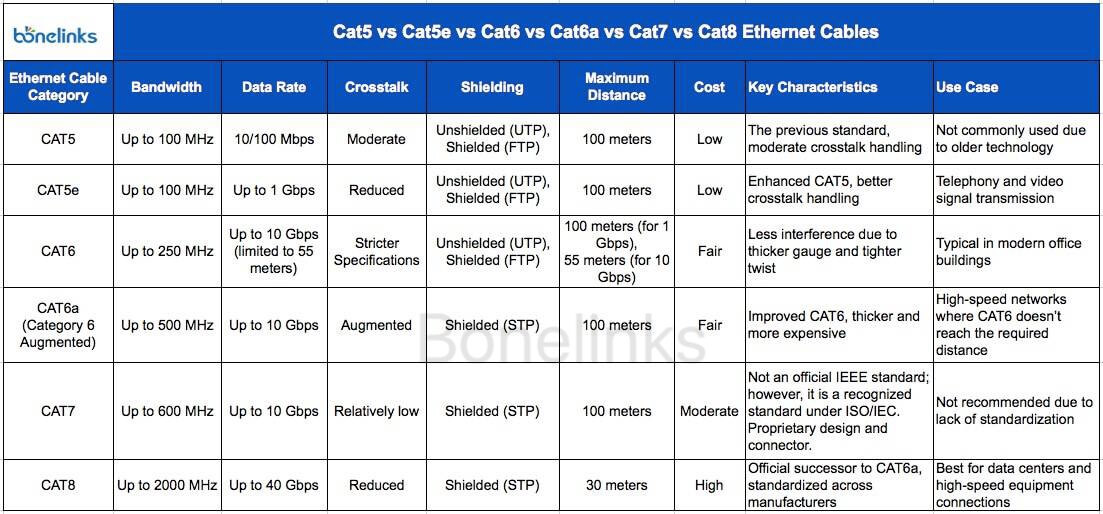
Cat5e
- Introduction: Since 1992, operates at 100 MHz, up to 100 Mbit, Class D Link.
- Pros: Affordable, easy installation, supports 1 Gbit, up to 2.5 Gbit with proper equipment.
- Cons: Legacy technology, inconsistent 1 Gbit performance.
Cat6
- Introduction: Original Gigabit Ethernet, 250 MHz, Class E Link.
- Pros: Better noise immunity, guaranteed 1 Gbit performance, supports up to 5 Gbit.
- Cons: Larger cable size, longer termination and testing.
Cat6a
- Introduction: Certified for 10 Gbit, 100x faster than Cat5, 500 MHz, Class Ea.
- Pros: Fastest copper network over any distance, backward compatible.
- Cons: Relatively expensive, larger cable size, complex testing.
Cat7 & Cat7a
- Introduction: Certified for 10 Gbit, 100x faster than Cat5, 600 to 1,000 MHz, Class F and Fa.
- Pros: Always shielded, higher operating frequency than Cat6a.
- Cons: Relatively expensive, larger cable size, complex testing, no significant speed advantage.
Cat8
- Introduction: Certified for 25 Gbit & 40 Gbit, 250 to 400x faster than Cat5, 2,000 MHz, Class II Cat8.2.
- Pros: Fastest copper network over any distance, not backward compatible.
- Cons: Relatively expensive, larger cable size, complex testing, max run length of 30-36 meters, for data centers.
Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat7a vs Cat8 Comparison
Cat5 vs Cat6 Ethernet Cable
The primary distinction between Cat 5 and Cat 6 lies in their transmission speed and bandwidth capabilities. Cat 5 cables typically operate at a transmission frequency of 100MHz, suitable for 100Mbps transmission rate applications. In contrast, Cat 6 cables boast a higher transmission frequency of 250MHz, making them apt for 1Gbps transmission rates and supporting Gigabit networks. This difference arises from Category 6 cables incorporating insulated crossbones within their internal structure, effectively isolating the four pairs of twisted pairs. This design enhances cable balance and diminishes signal crosstalk.
Cat5 vs Cat5e Ethernet Cable
The most notable distinction between Cat5 and Cat5e ethernet cables is their transmission speed. Cat5 cables offer a transmission speed of 100Mbps, whereas Cat5e cables provide a significantly faster rate of 1000Mbps (1Gbps), which is ten times that of Cat5. Additionally, Cat5e cables exhibit enhanced performance characteristics including reduced near-end crosstalk, improved attenuation crosstalk ratio, and better return loss. Despite these improvements, there isn’t a significant price difference between the two cable types. As a result, Cat5e ethernet cables have gradually replaced Category 5 cables in contemporary setups.
Cat5e vs Cat6 Ethernet Cable
Both Cat5e and Cat6 ethernet cables are capable of supporting transmission speeds of 1Gbps, which is generally sufficient for most home networks. However, if you’re aiming to upgrade to a higher 10Gbps network speed, Cat5e cables won’t suffice.
The primary distinction between Cat5e and Cat6 cables lies in their maximum transmission speed capabilities. Cat6 cables excel by supporting up to 55 meters of transmission distance at 10Gbps, making them suitable for more demanding applications. Despite their advantages, Cat6 cables tend to be around 20% pricier than Cat5e cables due to their advanced performance and features.
Cat6 vs Cat7 Ethernet Cable
When comparing Cat6 vs Cat7 ethernet cables, transmission frequency and cabling length stand out as crucial factors to consider. Cat6 cables offer a performance of up to 250 MHz, while Cat7 cables are rated for a transmission frequency of up to 600 MHz. In terms of cabling length, Cat6 supports a maximum of 100m at 1 Gbps, while Cat7 also reaches 100m but at 10 Gbps.
Regarding pricing, Cat7 cables are more expensive than Cat6 cables when compared under similar conditions. If both options are out of budget, Cat5e can be a suitable alternative for a 10G network.
Durability is another aspect that varies between Cat6 and Cat7. Cat6 cables have an estimated life cycle of around 10 years, whereas Cat7 cables are expected to last for approximately 15 years.
Cat7 vs Cat8 Ethernet Cable
When comparing Cat7 vs Cat8 ethernet cables, transmission frequency and cabling length remain significant factors. Cat7 cables offer a performance of up to 600 MHz, while Cat8 cables boast an even higher transmission frequency of up to 2000 MHz. In terms of cabling length, Cat7 supports a maximum of 100m at 10 Gbps, whereas Cat8 is limited to 30m but achieves higher speeds of 25 Gbps or 40 Gbps.
In terms of pricing, Cat8 cables are typically more expensive due to their unique features that set them apart from previous generations of Ethernet cables.
How to choose: Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7, Cat7a, or Cat8 cable?
General Office Use: Cat6 vs. Cat7
When comparing Cat6 and Cat7 for general office use, Cat7 offers slightly better data transmission and interference resistance due to its higher signal bandwidth. However, the history of Cat7 cables is a bit complex.
Initially designed for use with GG45 or TERA connectors, Cat7 cables are not fully backward-compatible with standard office equipment using 8P8C connectors (commonly known as RJ-45). Nevertheless, Cat7 cables can still carry Ethernet signals over the same wires as Cat6, with the option for cable manufacturers to create Cat7 cables with backward-compatible connectors.
Although the noise immunity of Cat7 cables can enhance performance and reliability, the choice depends on various factors. If you’re using Cat6 equipment and don’t anticipate significant performance gains, there’s no need to opt for Cat7. However, if you plan to upgrade to Cat7-specific equipment or value future-proofing, installing Cat7 cables might be a suitable choice.
The price difference isn’t substantial, and incremental upgrades allow you to mitigate resource commitment risks. In summary, consider your equipment plans and performance needs when deciding between Cat6 and Cat7 for your office setup.
General Office Use: Cat5e vs. Cat6
The Cat5e vs Cat6 debate is no longer relevant. When setting up a new network or upgrading an existing one, Cat5 should not even be a consideration. Your choice should be Cat6 cables, specifically Cat6a. This is a prime opportunity to replace any remaining Cat5 or Cat5e cables in your setup.
Home and Entertainment Use: Cat6 vs. Cat7
Similar considerations about Cat7 compatibility apply here as well. While improved noise immunity might offer advantages in demanding settings like hotels or entertainment venues, Cat6a cables are likely sufficient for most applications where Cat7 is considered.
Unless your equipment is explicitly designed for Cat7 cables, featuring GG45 or TERA connectors, opting for Cat7 over Cat6a cables might not yield significant benefits. Nevertheless, installing Cat7 cables can facilitate smoother future equipment upgrades and serve as a form of future-proofing.
Adding to the complexity, the telecom standardizing committee 3GPP introduced equipment categories, leading to some home LTE routers being labeled as Cat 7 equipment in LTE terms. However, this has no connection to the Cat7 cabling standard, and such routers don’t require Cat7 cables.
General Office/Entertainment Use: Cat6vs. Cat8, Cat7 vs. Cat8
For typical office and entertainment setups, utilizing Cat8 cables doesn’t usually offer practical benefits unless in data centers. The vast majority of office and entertainment equipment doesn’t require 25 Gbit/s or 40 Gbit/s connections, and the limited distance coverage of Cat8 cables is a significant constraint.
At lower speeds, Cat8 cables don’t provide substantial advantages compared to Cat7 or Cat6e.
Data Centre Use: Cat7 vs. Cat8
Considering Cat7’s complex history and the lack of official endorsement for 25 Gbit/s and 40 Gbit/s standards, Cat8 is typically the superior option. It offers higher speed and better future-proofing. Cat8 is the official choice by TIA/EIA for these modes and is designed specifically for data center applications. Cat8 Class II cables are also compatible with Cat7a equipment using GG45 or TERA connectors, ensuring compatibility with existing Cat7 equipment.
Specialized Applications: Cat7 vs. Cat8
Cat7 has found specialized niches beyond the typical use cases, particularly in specialized audio-video (AV) applications. The choice between Cat7 and Cat8 for these applications often depends on the specific equipment requirements. Cat8 Class II cables can work with Cat7a equipment, simplifying the decision if you’re already using Cat8 equipment.
Regardless of your choice, maintaining termination continuity is crucial, especially in structured cable installations. Mixing Cat7 network segments with Cat6a patch cables can create bottlenecks, so careful consideration is essential.
Anyway, choose the right Ethernet cable based on your specific needs:
- Home and Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) Networks: Opt for Cat5e as a minimum requirement for basic connectivity.
- Small to Medium-Sized Business: For businesses with multiple users and servers, Cat6 and Cat6a offer a cost-effective solution with sufficient bandwidth and performance.
- High-Speed Networking: If you require high-speed communication in a 25G or 40G network, consider Cat7 or Cat8 cables for faster speeds, durability, and reduced interference, enhancing overall productivity.
Final Words
After exploring various network cable types and distinctions, are you equipped to choose the ideal cable for your network? For queries or guidance, feel free to contact us. As a leading supplier of high-speed interconnectivity solutions, Bonelinks offers diverse Ethernet cables in varying lengths, colors, and styles. Our cables, made with pure copper, ensure reliable and high-speed network performance for your needs.




