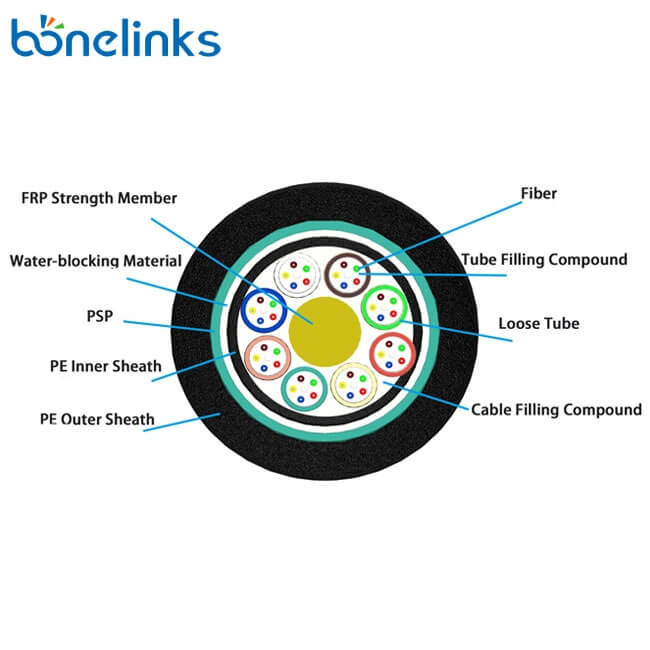
1. What is FRP Fiber Optic Cable?
FRP can also refer to the fiber reinforcement polymer used in fiber optic cables. Fiber optic cables are made up of glass or plastic fibers that transmit data using light signals. To protect the fragile fibers and provide mechanical strength, they are often reinforced with a central strength member made of a fiber reinforcement polymer (FRP) or steel.
2. How about FRP?
FRP stands for Fiber Reinforced Polymer, and it is a type of composite material that is commonly used in fiber optic cables as a strength member. The FRP provides mechanical support to the cable, which helps to prevent damage to the delicate fiber optic strands inside the cable. FRP is an attractive material for fiber optic cable because it is strong, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion and other environmental factors. It can also be easily molded into different shapes and sizes, making it adaptable to a wide range of cable designs.
3. Advantages of Using FRP in Fiber Optic Cables
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers several advantages for fiber cable applications.
3.1 Strength
FRP has a relative density ranging from 1.5 to 2.0, which is only a quarter to a fifth of that of carbon steel. Despite this, its tensile strength is comparable to or even higher than that of carbon steel. Furthermore, its specific strength can be likened to that of high-grade alloy steel. FRP offers high strength and stiffness, making it an ideal material for cable strength members. It can provide the necessary support to protect the fiber cables from external forces and prevent damage.
3.2 Lightweight
FRP is much lighter than steel or other metals, which can significantly reduce the weight of the fiber cable. For instance, a typical steel cable weighs 0.3-0.4 pounds per foot, while an equivalent FRP cable weighs only 0.1-0.2 pounds per foot. This makes it easier to handle, transport, and install the cable, particularly in aerial or suspended applications.
3.3 Corrosion-resistant
FRP is resistant to corrosion, which is particularly important in harsh environments, such as marine or underground applications. It can help protect the fiber cable from damage and extend its lifespan. In a study published in the Journal of Composites for Construction, FRP specimens subjected to harsh marine environments demonstrated minimal deterioration after a 20-year exposure period.
3.4 Non-conductive
FRP is a non-conductive material, which means it can provide electrical insulation for the fiber cable. This is particularly important in applications where electrical interference can affect the performance of the fiber cable.
3.5 Design Flexibility
FRP can be molded into different shapes and sizes, which can allow for more customized designs and cable configurations. This can help improve the efficiency and performance of the fiber cable.
4. FRP vs. Steel Strength Members vs. KFRP in Fiber Optic Cable
Three common materials used for the strength members in fiber optic cables are FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic), steel, and KFRP (Kevlar Fiber Reinforced Plastic). Let’s compare these materials based on their properties and characteristics.

4.1 Strength and Durability
- FRP: FRP strength members are made of composite materials such as glass or carbon fibers embedded in a plastic matrix. They offer good tensile strength and are lightweight, which makes them suitable for aerial installations. They are also resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them durable in harsh environments.
- Steel: Steel strength members are known for their high tensile strength and excellent durability. They are often used in outdoor installations where high mechanical strength is required, and they can withstand extreme weather conditions. However, steel is heavy and can be prone to corrosion over time, which may affect its longevity.
- KFRP: KFRP strength members are made of Kevlar fibers embedded in a plastic matrix. Kevlar is known for its exceptional strength and durability, and KFRP strength members provide high tensile strength with minimal weight. KFRP is also resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor installations.
4.2 Flexibility and Ease of Installation
- FRP: FRP strength members are flexible and easy to handle, making them ideal for installation in tight spaces or situations where flexibility is required. They can be easily bent or molded to fit various installation scenarios.
- Steel: Steel strength members are relatively stiff and less flexible compared to FRP and KFRP. They may require additional hardware or equipment for bending or shaping during installation, which can increase installation complexity and time.
- KFRP: KFRP strength members are highly flexible and easy to handle, similar to FRP. They can be bent or shaped during installation without the need for additional hardware, making them convenient for various installation scenarios.
4.3 Weight
- FRP: FRP strength members are lightweight, which can help reduce the overall weight of the fiber optic drop cable. This makes them suitable for aerial installations and situations where weight is a consideration, such as in overhead applications.
- Steel: Steel strength members are heavy, which can add weight to the fiber optic drop cable. This may not be ideal for aerial installations or situations where weight needs to be minimized.
- KFRP: KFRP strength members are lightweight, similar to FRP, which helps reduce the overall weight of the fiber optic drop cable. This makes them suitable for aerial installations and situations where weight is a consideration.
4.4 Electrical Conductivity
- FRP: FRP strength members are non-conductive, which can provide electrical isolation for the fiber optic cables. This can be advantageous in situations where electrical interference needs to be minimized.
- Steel: Steel strength members are conductive, which may pose a risk of electrical interference or grounding issues in certain installations.
- KFRP: KFRP strength members are also non-conductive, similar to FRP, which can provide electrical isolation for the fiber optic cables.
4.5 Cost
- FRP: FRP strength members are generally cost-effective compared to steel, making them a more affordable option for fiber optic drop cable applications.
- Steel: Steel strength members can be more expensive compared to FRP or KFRP, due to the cost of the material and additional manufacturing processes required.
- KFRP: KFRP strength members may be slightly more expensive than FRP, but still more cost-effective compared to steel. However, the cost may vary depending on the specific manufacturer and location.
5. Summary
FRP Fiber Optic Cable with a composite strength member offers advantages such as lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance. It is a reliable and cost-effective solution for telecommunication networks, making it an excellent choice for both indoor and outdoor applications. Upgrade your network with FRP Fiber Optic Cable today! Contact Bonelinks if you have any needs!