LAN cables have become ubiquitous across the globe. They are integral to establishing networks, whether for homes or businesses, by connecting to Ethernet ports on various network devices. This connectivity enables the seamless sharing of files, data, and information among these devices, while also facilitating Internet connections. In this blog, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that delves deeper into the world of LAN cables, enhancing your understanding of their significance.
What is LAN and LAN Cable?
LAN, or Local Area Network, is a private network comprising routers, cables, access points, switches, and other components. These elements enable devices to connect to web servers, internal servers, and even other LANs through Wide Area Networks (WAN). Setting up a LAN can be as simple as using an Ethernet cable.
So, what exactly is a LAN cable? It’s a networking cable that establishes connections between various devices. For instance, if you have a printer linked to your router with a cable, that cable is considered a LAN cable. These cables facilitate the connection of computers and hardware, creating a LAN, and are most effective for use over short distances.
What is the Role and Function of LAN Cable?
Primarily, a LAN cable is utilized to establish connections between devices within a network, employing a physical plug-in connection. Essentially, any data cable used for communication between end devices falls under the category of network cables.
Certain LAN cables are particularly well-suited for short distances. Their design often prioritizes space efficiency, enabling usage in confined spaces. In contrast, others are designed for extended distances or outdoor applications.
However, the core purpose of all these cables remains consistent: connecting devices with network connectors. Beyond computers, routers, or servers, peripheral devices like printers or IP cameras are also integral parts of the network.
To achieve this, a LAN cable is connected to a terminal device. The data is transmitted to the other end device via a LAN distributor, which must also be seamlessly integrated into the network infrastructure.
What is the Appearance of a LAN Cable?
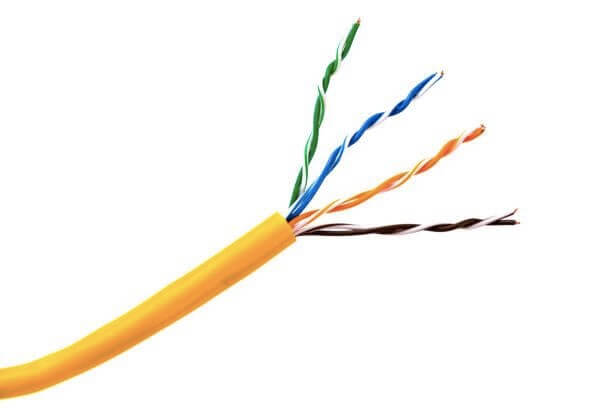
Externally, a LAN cable shares a resemblance with a telephone cable. It is encased in a plastic sheath, commonly coming in colors such as blue, orange, yellow, or gray. Within the sheath are eight individual strands, which are further organized into four pairs of wires.
A notable feature of network cables is their consistent appearance at both ends. Equipped with RJ45 plugs, these connectors have a rectangular shape and often feature a small tab for locking into Ethernet ports.
Moreover, these plugs incorporate a small LED indicator. This light can signify activity on the connected device. For instance, a green light indicates successful network connection, while a red light indicates an error. While the light is illuminated, it signifies ongoing communication between the device and the LAN distributor.
What is a LAN Port?
LAN ports are integral components of computers, servers, and other network-enabled devices. These ports look somewhat similar to the telephone connection and typically utilize the standard RJ45 cable connector, which is widely used across various devices.
Ethernet port sockets are typically located at the back of routers or PCs, while laptops often have them on the sides. Due to the compact design of modern notebooks, these ports might not be available everywhere. However, adapters can be employed to address this limitation.
The primary function of a LAN port is to provide a wired access point to a network. It’s important to note that a wireless network cannot be directly established using a LAN port.
Is LAN Cable the Same as Ethernet Cable?
To address this question, it’s important to first clarify the concept of Ethernet, as the distinctions, while subtle, hold significance.
Ethernet denotes wired data transmission within a local area network (LAN). Devices within this network are interconnected through a cable, commonly referred to as a LAN cable.
Initially, the term “Ethernet cable” served as a generic label, encompassing different types of cables. Specifically, it referred to a twisted copper cable. Data transmission adhered to standardized protocols, with information packaged into Ethernet frames containing data, checksums, and MAC addresses.
While Ethernet is a widely adopted standard, other protocols like Arcnet and Token Ring have existed but were largely replaced by Ethernet due to its superior performance and adoption.
LAN Cable vs Ethernet Cable: Is there any Difference?
In simple terms, “LAN” refers to a specific area covering a few hundred meters. LAN cables play the role of connecting various network components like computers, switches, routers, or printers.
“Ethernet” covers the whole networking system, including cabling, protocols, and standardized plugs. Ethernet cables come in different lengths, colors, and speeds.
However, they all share a common feature: an RJ45 connector at both ends, which links devices together.
In reality, the terms “LAN cable” and “Ethernet cable” are often used interchangeably, with no practical differences in procurement. When buying a network cable, whether you see “LAN cable” or “Ethernet cable,” both refer to a twisted copper cable for networking purposes.
LAN Cable vs Patch Cable: Are they the Same?
A patch cable, like a LAN cable, falls under the category of network cables. While there isn’t a precise definition, the term “patch cable” generally refers to shorter cables. These cables are typically used in non-permanent installations, commonly in office settings and similar environments.
Patch cables serve the purpose of connecting devices within a network and are characterized by their shorter length.
These cables can be procured pre-terminated, meaning they come already assembled. On the other hand, installation cables are often provided without RJ45 connectors and need to be adapted later. However, modern manufacturing ensures high-quality “ready-made” patch cables are readily available and reliable.
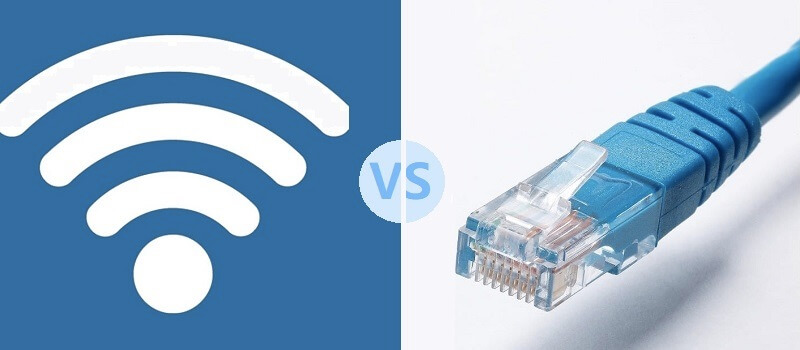
LAN Cable vs Wi-Fi: What is the Difference?
The most significant contrast between a LAN cable and Wi-Fi is their physical nature. In the purest sense, LAN entails a physically interconnected network utilizing cables, while Wi-Fi functions as a wireless network.
Wi-Fi, which stands for Wireless Fidelity, serves as a standard designated for devices capable of receiving WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network). This standard is endorsed by the Wi-Fi Alliance, a consortium of companies specializing in research within this domain.
Despite often being used interchangeably, it’s crucial to distinguish between Wi-Fi and WLAN. Precisely, the latter refers to the broad term encompassing wireless local area networks, while Wi-Fi pertains to the specific device standard conforming to this technology.
LAN vs WLAN: Which is Faster?
When it comes to transmission speed, LAN cables hold a significant advantage over WLAN. Present-day standards enable transmission rates of up to 40 Gb/s in wired networks. This speed far surpasses what is achievable in wireless networks.
Even with the latest Wi-Fi 6 standard (WLAN AX), theoretical data streams of up to 9.6 Gb/s can be attained. Nonetheless, this is primarily a theoretical value and real-world performance is hindered by external interference factors, making it challenging to achieve consistently.
Types of LAN Cables
LAN cables come in two main materials: copper and fiber optics. Each material has its distinct attributes:
- Copper Cables: Copper LAN cables are commonly used and are cost-effective. They are available in various categories like Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, and Cat 7. While they offer reliable data transmission, they are susceptible to interference over longer distances.

- Fiber Optic Cables: Fiber optic LAN cables are known for their high-speed transmission and greater bandwidth. They are notably thin, resistant to interference, and suitable for longer distances. Although they offer superior performance, they tend to be more expensive than copper cables.

Advantages and Disadvantages of LAN Cabling
Advantages
- Faster and More Stable Data Transmission: Ethernet cables offer quicker and more consistent data transmission compared to wireless networks (WLAN).
- Reduced Interference: They are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference, ensuring a more reliable connection.
- Versatility: Standardized plugs and sockets make them versatile and compatible across various devices.
Disadvantages
- Cable Thickness and Cost: LAN cables can be thicker and more costly to install, especially in larger network setups.
- Limited Bending Radius: Their bending radius is smaller compared to other cable types like fiber optic cables.
- Reduced Mobility: LAN connections lack the mobility of WLAN, as users are tethered to a specific location.
Why I Should Use a LAN Cable to Access the Internet?
While LAN cables offer advantages, they excel in terms of security when compared to WLAN setups. Wireless networks can be vulnerable to unauthorized access through cracking attacks or signal jamming. In contrast, LAN connections require physical access to the network for potential hacking attempts, providing a higher level of security.
What Factors to Consider Before Purchasing LAN Cables?
When it comes to purchasing LAN cables, there’s no universal solution. The considerations to keep in mind are highly dependent on your specific network setup. Here are some guidelines for your reference:
- Begin by assessing your home or office network’s speed. If your internet operates at 1Gbps, using an outdated LAN cable could limit your performance. For slower internet connections between 10 to 20 megabits per second, a Cat 5 cable or newer models can suffice. Cat6 cables have gained popularity as a versatile standard suitable for both residential and commercial environments.
- Determine your desired transmission speeds. Longer LAN cables generally have slower transmission speeds compared to shorter ones. The 100-meter rating is typically applicable to larger professional installations.
- Prioritize sturdy LAN cables. Modern routers are equipped with increased capabilities for faster network speeds. Therefore, selecting robust LAN cables can enhance network speed and future-proof your setup.
- To minimize interference, consider SF/FTP cables. These cables incorporate shielding, twisting, and double external protection to mitigate potential disturbances.
Conclusion
All in all, a LAN cable facilitates the connection of your networking devices through wireless routers or alternative network switches. It’s essential to opt for the optimal LAN cable type that aligns with your requirements and effectively fulfills your needs.