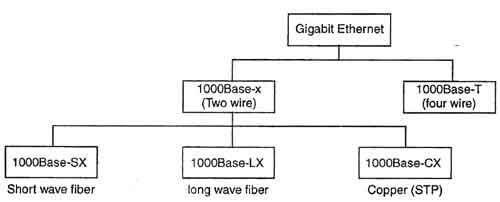
Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) has gained significant popularity and is widely used in enterprise network backbones. It’s defined by IEEE standards 802.3z, 802.3ab, and 802.3ap. These standards are vital for Ethernet’s physical layer and encompass various 1000BASE-X specifications like 1000BASE-T, 1000BASE-CX (Copper), 1000BASE-KX, 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX, 1000BASE-EX, and 1000BASE-ZX.
This post will concentrate on specific fiber optic transmission standards, including 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX, 1000BASE-EX, and 1000BASE-ZX.
What is 1000BASE-X?
1000BASE-X is an Ethernet communication standard that enables data transmission at speeds up to 1 Gbps (Gigabits per second) using either a single fiber optic cable or a pair of copper wires.
Breaking it down:
- “1000” designates a transmission speed of 1,000 Mbps.
- “BASE” indicates Ethernet baseband signaling as the standard.
- “1000BASE” refers to a Gigabit Ethernet connection.
- The letter “X” specifies the block coding used for Gigabit Ethernet.
Specific standards under 1000BASE-X include:
- 1000BASE-SX: “S” represents short-range multi-mode optical cable (less than 100 meters).
- 1000BASE-LX: “L” signifies long-range single- or multi-mode optical cable (ranging from 100 meters to 10 kilometers).
- 1000BASE-EX: “E” extends the reach, supporting distances up to 40 km over single-mode fiber, using non-standard industry optics.
- 1000BASE-ZX: Achieves distances of at least 70 km over single-mode fiber, also utilizing non-standard industry optics.
What is 1000BASE-SX?
1000BASE-SX is a gigabit Ethernet standard that operates over fiber optic connections. It is designed for use on multimode fiber with a short wavelength range of 770 to 860 nanometers (typically 850nm). The “SX” in its name signifies its suitability for short reach distances on multimode fiber.
Specifics of 1000BASE-SX include:
- A maximum length of 220 meters for 62.5μm fiber distributed data interface (FDDI) multimode fiber. A maximum length of 275 meters for 62.5μm/200MHz·km multimode fiber.
- A maximum length of 550 meters for 50μm/500MHz·km multimode fiber.
- Support for distances of up to 1 kilometer over laser-optimized OM3, OM4, or OM5 multimode fiber.
This standard finds extensive use in environments like large office buildings, co-location facilities, and carrier-neutral Internet exchanges.
What is 1000BASE-LX?
1000BASE-LX is a gigabit Ethernet standard designed for fiber optic connections. It is suitable for operation on both single mode fiber (SMF) and multimode fiber (MMF) and utilizes a long wavelength range of 1270 to 1355 nanometers (typically 1310nm). The “LX” designation indicates its capability for long reach connections.
Key features of 1000BASE-LX include:
- Support for up to 10 kilometers over single mode fiber.
- Some vendors offer extended distances of up to 20 kilometers, beyond the standard specification.
- With multimode fiber, it can reach a maximum distance of 550 meters. Note that certain link distances above 300 meters may require a specific conditioning patch cord.
Due to its extended reach, affordability, and compatibility with various fiber types, 1000BASE-LX has gained popularity as a widely adopted standard in enterprise networks.
What is 1000BASE-EX?
1000BASE-EX is a commonly used industry term for Gigabit Ethernet fiber optic transmission, even though it is not a standard designation. The “EX” in its name signifies its ability to extend reach, supporting distances of up to 40 kilometers over single mode fiber.
Key features of 1000BASE-EX include:
- Utilizes the same long wavelength of 1310nm as 1000BASE-LX.
- Offers a higher power budget compared to 1000BASE-LX, allowing for longer distances.
- Sometimes referred to as 1000BASE-LH (Long Haul) by certain manufacturers.
Due to its capability to cover longer distances, 1000BASE-EX often involves higher costs for optical components, resulting in a higher price point compared to 1000BASE-SX and 1000BASE-LX standards.
What is 1000BASE-ZX?
1000BASE-ZX is a widely used industry term for extended-distance Gigabit Ethernet transmission, even though it is not an official standard. It supports distances of up to 70 kilometers (43 miles) over single mode fiber, utilizing a long wavelength of 1550 nm.
Key points about 1000BASE-ZX include:
- Operates with a 1550 nm long wavelength on single mode fiber.
- Transceiver vendors often offer versions that cover 80 kilometers (50 miles) as an enhanced option.
- Some manufacturers provide transceivers labeled as 1000BASE-EZX or 1000BASE-ZX120, enabling distances of up to 120 kilometers (75 miles) using single-mode fiber.
It’s important to note that 1000BASE-EZX transceivers feature high transmitter power and receiver sensitivity. To prevent bit errors due to overload, proper fiber attenuators should be added when using these transceivers.
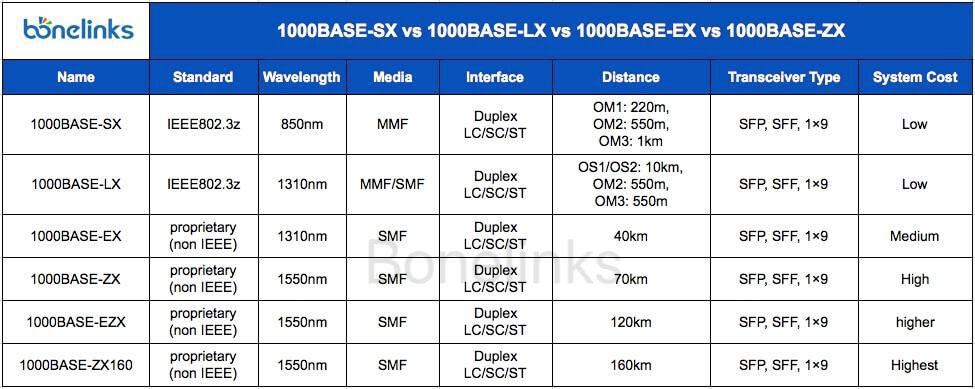
1000BASE-SX vs 1000BASE-LX vs 1000BASE-EX vs 1000BASE-ZX
Conclusion
Indeed, the various 1000BASE-X standards cater to different fiber optic cabling needs based on their transmission distances and cost considerations.
- 1000BASE-SX is optimal for multimode fiber cabling, offering a cost-effective solution with a limited reach. It’s suitable for short-distance transmissions typically within buildings or data centers.
- 1000BASE-LX, 1000BASE-EX, and 1000BASE-ZX are tailored for single mode fiber cabling, catering to longer distances required for backbone networks. They provide greater reach while offering options for extended distances, making them suitable for interconnecting networks over larger geographic areas.