Mobile communication base station is a form of radio station, which refers to a radio transceiver station that transmits information between mobile phone terminals through a mobile communication exchange center in a certain radio coverage area.
The construction of mobile communication base stations is an important part of the investment of mobile communication operators, and is generally carried out around factors such as coverage, call quality, investment benefits, construction difficulty, and maintenance convenience.

In order to facilitate the distinction between the concepts and characteristics of different mobile communication base stations, Bone links will analyze macro base stations, distributed base stations, SDR base stations, and repeaters one by one.
Macro Base Station
A macro base station refers to a wireless signal transmitting base station of a communication operator. A macro base station has a large coverage distance, generally 35 km, and is suitable for suburban areas with dispersed traffic. It has omnidirectional coverage and high power.
A micro base station is mostly used in cities with a small coverage distance, generally 1-2 km, and directional coverage. A micro-micro base station is mostly used for blind spot coverage in urban hotspots. Generally, the transmission power is very small and the coverage distance is 500m or less.

The power of macro base stations is generally 4-10W, which is converted into a wireless signal ratio of 36-40dBm, plus the gain of the base station coverage antenna of 20dBi, which is 56-60dBm.
If such power is irradiated on a person, no one can bear it. However, there is a lot of air, dust, various sounds and various objects in the area where we live, which can block a lot of electromagnetic radiation, so when the high-power electromagnetic waves are emitted from the base station antenna and reach us, they have become very weak.
Distributed Base Stations
Distributed base stations are a new generation of modern products used to complete network coverage.
Its main feature is that the RF processing unit is separated from the traditional macro base station baseband processing unit while being connected through optical fiber. The core concept of the distributed base station structure is to separate the traditional macro base station baseband processing unit (BBU) and the RF processing unit (RRU), and the two are connected through optical fiber.
During network deployment, the baseband processing unit is concentrated in the computer room with the core network and wireless network control equipment, and connected to the RF remote unit deployed on the planned site through optical fiber to complete network coverage, thereby reducing construction and maintenance costs and improving efficiency.

Distributed base stations divide traditional macro base station equipment into two functional modules according to their functions. The baseband, main control, transmission, clock and other functions of the base station are integrated into a module called baseband unit BBU (Base Band Unit). The baseband unit is small in size and has a very flexible installation location.
By integrating the transceiver, power amplifier and other intermediate radio frequency into another module called remote radio frequency, the radio frequency unit RRU (Remote Radio Unit) is installed at the antenna end. The radio frequency unit and the baseband unit are connected by optical fiber to form a new distributed base station solution.

SDR Base Station
“DR (Software Defination Radio) is a wireless broadcast communication technology, or more precisely, a design method or design concept. Specifically, SDR refers to a wireless communication protocol based on software definition rather than implemented through dedicated hardware.
Currently, there are three mainstream SDR hardware platform structures: SDR structure based on GPP, SDR (Non-GPP) structure based on field programmable gate array (FPGA), and hybrid SDR structure based on GPP + FPGA/SDP. The SDR structure based on GPP is as follows:

The SDR base station is a base station system designed and developed based on the SDR concept. Its biggest feature is that its radio frequency unit has the ability to be programmable and redefined, which can realize intelligent allocation of spectrum and support multiple network modes, that is, it can realize technology of different network modes on the same platform device.
Repeater
A repeater is a device that connects network lines and is often used for bidirectional forwarding of physical signals between two network nodes. It is mainly composed of antennas, RF duplexers, low noise amplifiers, mixers, electrically adjustable attenuators, filters, power amplifiers and other components or modules, including uplink and downlink amplification links.
Repeaters are the simplest network interconnection devices. They mainly perform the functions of the physical layer, and are responsible for transmitting information bit by bit on the physical layer of two nodes, completing the functions of signal replication, adjustment and amplification, so as to extend the length of the network. Due to the existence of losses, the power of the signal transmitted on the line will gradually attenuate. When the attenuation reaches a certain level, it will cause signal distortion, thus causing reception errors.
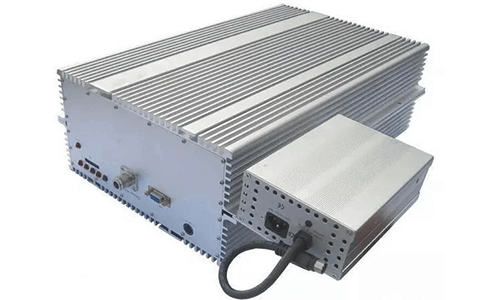
The basic principle of its operation is: the forward antenna (donor antenna) receives the downlink signal of the base station into the repeater, amplifies the useful signal through the low noise amplifier, suppresses the noise signal in the signal, and improves the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N); then down-converts to the intermediate frequency signal, filters through the filter, amplifies the intermediate frequency, and then up-converts to the radio frequency, amplifies through the power amplifier, and transmits to the mobile station through the backward antenna (retransmission antenna).
At the same time, the backward antenna receives the uplink signal of the mobile station, and is processed by the uplink amplification link along the opposite path: that is, it passes through the low noise amplifier, down converter, filter, intermediate amplifier, up converter, power amplifier, and then transmits to the base station. Thus, two-way communication between the base station and the mobile station is achieved.
A repeater is a wireless signal relay product. The main indicators for measuring the quality of a repeater include the degree of intelligence (such as remote monitoring, etc.), low IP3 (the WLAN standard stipulates that it is less than -36dBm), low noise factor (NF), overall reliability, and good technical services.
Commonly used repeaters include mobile phone signal repeaters, mobile phone signal amplifiers, etc. Taking the Fengxintong mobile phone signal amplifier as an example, it refers to a radio transmission relay device that plays a role in signal enhancement during wireless communication transmission. Its basic function is a RF signal power enhancer.
In the downlink, the main antenna picks up the signal from the existing coverage area. The bandpass filter isolates the signal outside the bandpass very well, and the filtered signal is amplified by the power amplifier and then transmitted to the area to be covered. In the uplink path, the signal of the mobile phone in the coverage area is processed by the uplink amplification link in the same way and then transmitted to the corresponding base station, so as to achieve signal transmission between the base station and the mobile phone.
The use of repeaters is one of the necessary means to achieve the goal of “small capacity, large coverage” mainly because the use of repeaters can ensure network coverage without increasing the number of base stations, and secondly, its cost is much lower than that of micro-cellular systems with the same effect. Repeaters are an optimal solution to solve the problem of extending the coverage capacity of communication networks.
Compared with base stations, it has the advantages of simple structure, less investment and easy installation. It can be widely used in blind spots and weak areas that are difficult to cover, such as shopping malls, hotels, airports, docks, stations, stadiums, entertainment halls, subways, tunnels, highways, islands and other places to improve communication quality and solve problems such as dropped calls.
In Summary
Base stations have gone through the development process from analog to digital, from narrowband to broadband, and are updated every 4 to 5 years. However, its development direction has not changed. In terms of form, future base stations will develop in three directions: macro base stations with higher performance and integration, micro base stations with smaller size, and more flexible distributed base stations. In terms of composition architecture, various base stations will become open modular products: in terms of technology, future base stations will develop in the direction of higher integration, full IP, multi-carrier and more efficient digital power amplifier.
As nodes for data transmission and connection of base stations, RRU and BBU fiber optic jumpers with IP68 waterproof connectors play an important role. In addition, outdoor armored optical cables used for laying backbone and access end networks are also commonly used in the construction of mobile communication base stations. If you want to know more about the optical fiber jumpers and fiber optic connectors used to connect base stations, please send us a message at www.bonelinks.com.




