1. What is FTTR?
Before talking about FTTR, let’s talk about what FTTx is.
FTTx is the abbreviation of “Fiber To The x”, which refers to “Fiber To The x”, where x not only represents the location where the fiber reaches, but also includes the optical network equipment installed at the location, and specifies the area served by the network equipment. For example, “H” in FTTH is the abbreviation of Home, which refers to fiber to the home. The home optical cable is laid out to the user’s home, and the modem is installed in the user’s home. The area served by the modem is one family.
The “R” in FTTR is the abbreviation of Room, which refers to the fiber to two or more rooms in the user’s house, and the installation of modem in the corresponding rooms. FTTR (Fiber to The Room) refers to replacing network cables with optical fibers, laying optical fibers in each room. It is a new coverage mode for home networks in the Gigabit era. Each modem serves one or more rooms in the home.
2 Why need FTTR?
2.1 Current situation of WiFi coverage in home broadband users
Most of home broadband users’ indoor WiFi is connected to a router through a modem, and covered by the router’s WiFi signal.
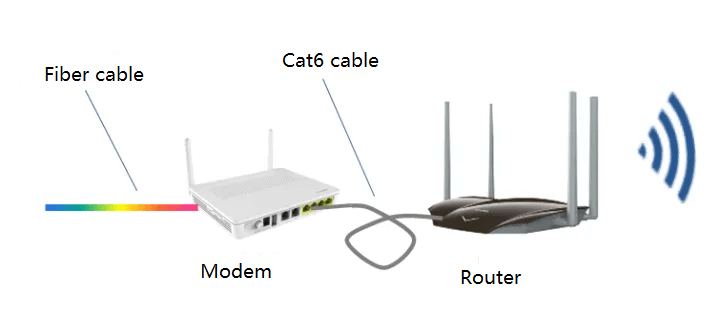
Routers generally support 2.4G and 5G frequency bands. Although the 2.4G frequency band can support a maximum rate of 300Mbps, due to the relatively large interference in this frequency band, the actual use effect is much worse. The high-bandwidth applications of users must use the 5G frequency band, but the WiFi signal in the 5G frequency band has a weak ability to penetrate walls, which brings great inconvenience to the high-bandwidth applications of some large-scale users.
In simple terms, Gigabit optical network is like a highway. FTTH paves the road to the house’s door, while FTTR paves the road to every room. FTTR resolves indoor WiFi coverage issues and eliminates WiFi congestion.
2.2 Inadequacies of existing whole home WiFi coverage solutions
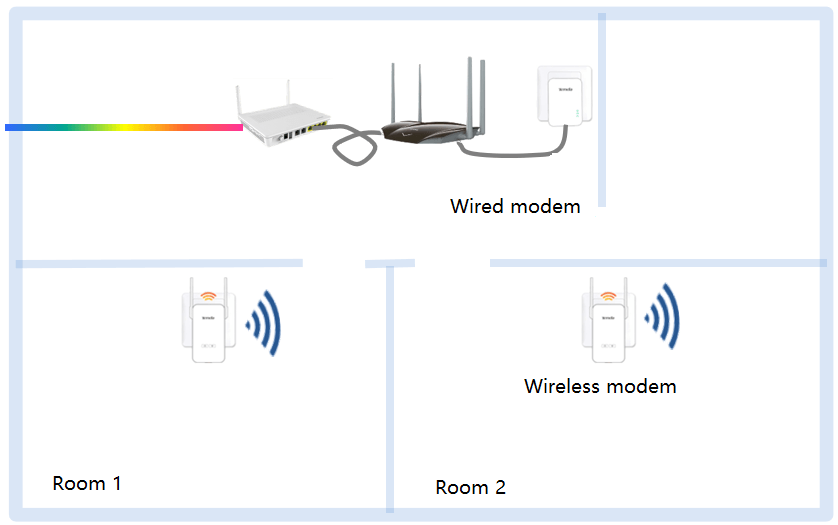
At present, the whole-home WiFi coverage solutions mainly include three types: router cascade, PLC power line communication, and child-parent router.
The router cascading solution is to set the master router at the modem, and set up the slave router in each room, and connect the master and slave routers with Cat6 cables. Restricted by the number of LAN ports of the master router, the number of slave routers does not exceed 4. If it exceeds, a switch should be added at the master router. Because this solution adopts wired connection, it can ensure the gigabit connection between the master and slave routers. The disadvantage is that Cat 6 wires need to be placed in the house, which is difficult to layout and may look messy.
Modems are divided into wired modems and wireless modems. The wired modem is connected to the LAN port of the router with a Cat 6 cable; the wireless modem is a wireless router that can be plugged into any power socket in the house (preferably a wall socket), and one wired modem can be paired with multiple wireless modems. The signals between the wired power modem and the wireless power modem are transmitted through the power line. The network speed is greatly affected by the quality of the user’s indoor power line wiring, and the terminal is often disconnected when each AP is roaming.
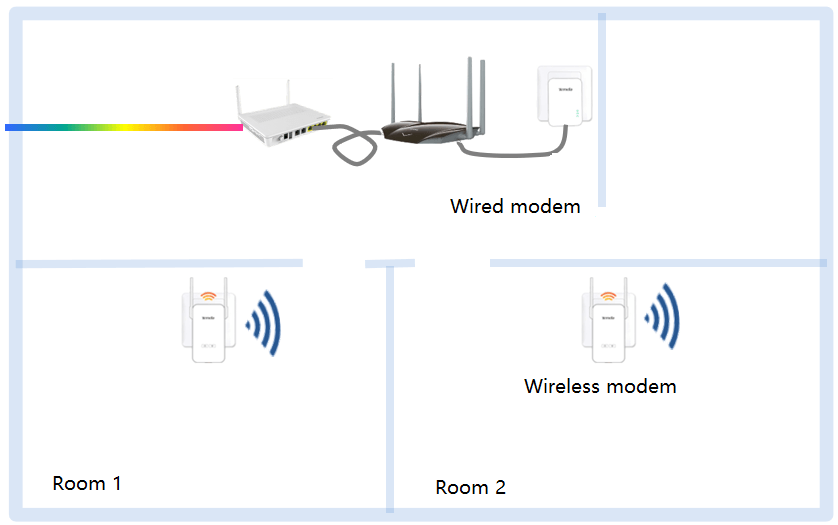
The parent-child routing solution includes a parent router and multiple child routers. Mesh networking can be performed between the routers through WiFi. Since it is difficult for WiFi signals between routers not to pass through walls, the bandwidth capability of this solution is greatly affected by the environment, and so comes the child-parent routing product. Both the child and the parent routers use WiFi and power lines for transmission, which improves the WiFi penetration capability to a certain extent. However, compared with the router cascade solution, the overall bandwidth capability is still significantly different.
2.3 Advantages of FTTR
FTTR Fiber To The Room uses one master modem and multiple slave modems for indoor WiFi coverage, and the master and slave modems are connected by bow-type drop cables for access network.
Compared with the above solutions, FTTR has the following advantages:
- Bow-type drop cables for access networks are easier to lay than Cat6 cables, and the layout of bow-type drop cables for access networks basically does not affect the indoor appearance
- High bandwidth and high speed. The maximum network speed near any modem of Gigabit users can reach 1000Mbps
- The network speed is stable, and the terminal switches smoothly between modems
- FTTR enables intelligent operation and maintenance, visualizing the network, improving Wi-Fi experience, and targeting potential customers for effective home network promotion
- FTTR enables seamless whole-house WiFi roaming with multiple slave OTN access points under one SSID. The master OTN quickly switches wireless devices to access points with better signals within 100ms for improved connectivity.
- The life of the optical fiber is more than 20 years for long time use
Due to the above advantages of FTTR, at present, the whole-home WiFi coverage solution provided by the operator is being adjusted from the previous child-parent routing solution to the FTTR solution.
3. FTTR solutions
FTTR revolutionizes home networking with gigabit coverage in every room, ensuring low latency, high quality, and stable Wi-Fi 6 performance throughout the house. It’s a significant technological upgrade, bringing optical fiber to every corner for superior connectivity in the gigabit era.
According to the difference in the optical fiber connection method between the master and slave modems, the solutions of FTTR are divided into P2P solutions and P2MP solutions.
3.1 P2P FTTR solution
The P2P solution is based on Ethernet technology. An optical fiber connects the master modem and each slave modem. The master modem is generally equipped with 4 single-core bidirectional optical modules, which can connect up to 4 slave modems. Compared with the router cascading solutions, the biggest change in this solution is to change the cascading RJ45 interface to an optical interface, so that optical fiber transmission can be used between the master and slave routers. The technology is simple to implement and low cost, but has limited scalability.
3.2 P2MP FTTR solution
The P2MP solution is based on GPON technology. The master modem is equivalent to a mini OLT, and the configured optical module is a Class B+ optical module common to GPON; the slave modem is the WiFi 6 Gigabit modem currently used by GPON. A 1:5 optical splitter is used in the ODN between the master and slave modems. The splitter can be cascaded in multiple stages and supports the access of up to 16 slave modems.
More interesting is this 1:5 optical splitter. The splitter adopts unequal split light, the insertion loss between the input port and the cascade port is about 2.0dB, and the insertion loss between the input port and the output port is about 15.4dB. Each splitter includes 1 input port, 1 cascade port and 4 output ports, and each output port can be connected to 1 slave modem.
3.3 Comparison of P2P and P2MP FTTR solution
The P2P solution is simple in technology and cheap in price. Although the number of modems supported is relatively small, judging from the current installed FTTR users, most users have less than 4 modems. Therefore, the P2P solution can basically meet the needs of users.
P2MP adopts GPON technology, which saves the deployment of optical fibers. It supports many slave modems, and the increase or decrease of slave modems is also very convenient. Although the price of the master modem is relatively high, due to operation, maintenance and management are more convenient, and it has become the leading solution recommended by operators.
4. FTTR implementation cases
The house type of a gigabit FTTH user is shown in the figure below, and the modem and WiFi 6 router are installed in position 1. Points D and F without a partition wall from the router have faster network speeds, points A, C, and E separated from the router by one wall have less than half the network speed of point D, and points B and G separated from the router by two walls. The internet speed at the point is less than 20% of point D.
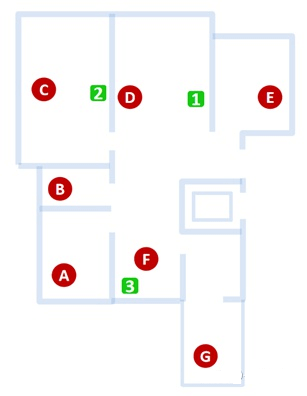
Carry out FTTR Fiber To The Room transformation for this user, and set up a slave modem in position 1, 2, and position 3 respectively (the main modem does not support WiFi). The network speed of points A to G in the 5G frequency band was tested, and compared with the speed of FTTH.
In order to test the transmission performance of the slave modem, in FTTH mode, the network speeds of “master modem + router” and “master modem + slave modem (only 1)” were tested respectively.
Place | FTTH (Unit: Mbps) | FTTR (Unit: Mbps) | |
From the modem | From the router | From the modem | |
A | 235 | 221 | 474 |
B | 121 | 125 | 230 |
C | 240 | 273 | 629 |
| D | 620 | 622 | 616 |
| E | 270 | 277 | 358 |
| F | 480 | 440 | 699 |
| G | 45 | 91 | 326 |
It can be seen from the comparison of the network speed of the two solutions of FTTH, when the coverage is small, the transmission performance of the modem is almost the same as that of the mainstream WiFi 6 routing (the stability of the router in multi-terminal access is higher than that of the modem).
In this case, the area of the user’s house is about 130 square meters, the structure of the house is not complicated, and the location of the FTTH modem and the router is relatively moderate, so the comparison between FTTR and FTTH network speed is not very different. However, the advantages of FTTR will be more prominent in large flats, villas, and duplex rooms with more than 4 bedrooms and 2 halls and a larger total area.

5. FTTR business model
FTTR (Fiber to the Room) extends optical cables into every room, making home networking more advanced. There are two scenarios:
“Post-decoration” – Install optical fibers in occupied houses, which can be challenging due to existing infrastructure. Sometimes, only open wires can be used.
“Before-decoration” – Deploy fiber networks before users move in, allowing flexible planning and easy installation. All-optical cables are routed through dark pipes, and there will be no open-line deployment.
The “before-decoration” model is simpler and risk-free, ensuring optimal Wi-Fi coverage and aesthetics. Collaborating with decoration and real estate companies, FTTR can be implemented in well-decorated houses, attracting high-value users and promoting home network development. By allowing operators to enhance the customer broadband experience, FTTR enables telcos to significantly improve their FTTH business models. It’s a win-win for all, driving the advancement of home networking infrastructure.
6. At the end
At present, FTTR is mainly promoted by operators in the form of packages, and some users do not just need it. Although the experience of most FTTR users has been improved compared with before, the user experience can also be improved through the parent-child routing solutions.
Among the two technical solutions of FTTR, P2MP will eventually become the mainstream solution. The strong access capability of this solution can even be used for the internal networking of small and micro enterprises, as well as the access of larger user groups such as hotels, restaurants, and supermarkets. In this solution, the multi-level cascade method of 1:5 unequal splitter can also be used in low-density access scenarios such as rural areas. It is expected that the FTTR technology based on P2MP will have a wider range of applications.
Bonelinks provides FTTR fiber cables, contact us ([email protected]) if needed.




