What is a fiber optic network?
Fiber optic network refers to the connection between the user network interface and the related service node interface.
The whole process uses optical fiber as the transmission medium or optical fiber as the backbone transmission medium, and metal wire or wireless as the transmission medium at the end of an access bearer.
Figure 1 shows the location of the fiber optic network in the whole telecommunication network.
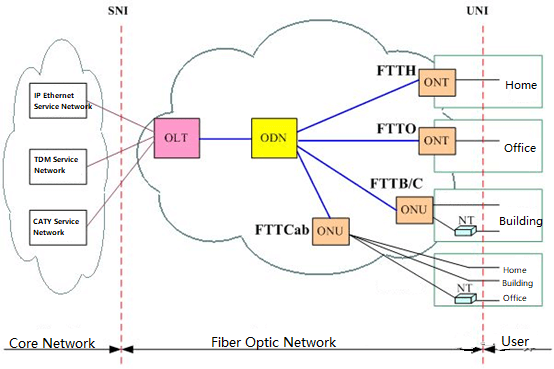 Figure 1
Figure 1
The technologies used in the fiber optic network include xPON, MSTP, MSAP, Ethernet, PTN, and optical fiber direct connection. OLT, ONT, and ONU in Figure 1 respectively refer to optical line terminals, optical network terminals, and optical network units, and generally refer to central office equipment and user-end equipment in various technologies, not just the use of xPON technology.
ODN refers to a passive optical distribution network composed of optical fiber cables and passive optical components (such as optical connectors and optical splitters) between OLT and ONU/ONT, mainly composed of optical cable lines in different sections. When the xPON technology is used, the ODN includes an optical splitter, as shown in Figure 2. When the passive wavelength division technology is used, the ODN includes an optical terminal multiplexer OTM or an optical add-drop multiplexer OADM.
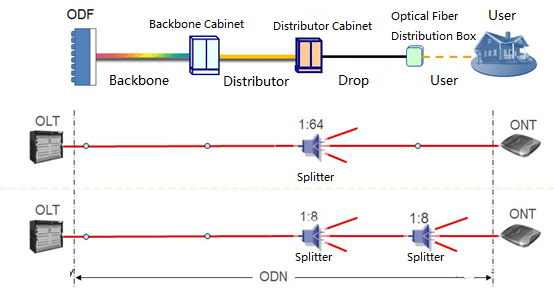
Figure 2
Typical application types of fiber optic network
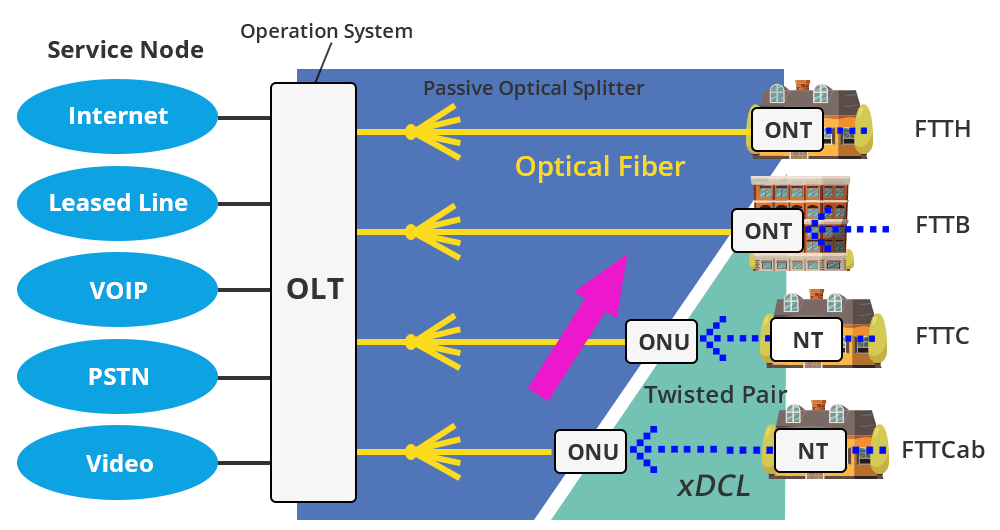
Fiber optic network includes typical applications such as FTTH, FTTO, FTTB/C, and FTTCab, commonly known as FTTx.
- FTTH refers to fiber-to-home. It is an access method that only uses optical fiber transmission medium to connect the communication office and the family house. The user optical cable is exclusively used by a single house.
- FTTO refers to fiber to the office. It is an access method that only uses the optical fiber transmission medium to connect the communication center and the company or office. The user fiber optic cable is exclusively used by a single company or office user, and the equipment and network after the ONT are managed by the user.
- FTTB/C refers to fiber-to-the-building/fiber-splitting cassettes. After fiber-to-the-building, the ONU is set in a suitable location, and then provides access services for users through metal wire pairs or wireless. Each ONU typically supports ten to one hundred users individually. The concept of FTTB/C has been basically replaced by FTTB at present.
- FTTCab refers to the fiber to the cabinet. The ONU is installed in the outdoor cabinet. After the optical cable is laid in the cabinet, it provides access services for users through metal wire pairs. Each ONU typically supports hundreds to thousands of users. At present, the FTTCab method is basically no longer used.
Although FTTx refers to “fiber to x”, its meaning includes not only the deployment of optical fibers to the x location, but also the setting location of the ONU/ONT. The difference between ONU and ONT is: ONT is a type of ONU, ONU is usually shared by multiple users, while a single user exclusively shares ONT. Therefore, the user-side equipment in FTTH and FTTO applications is usually represented by ONT, while in FTTB and FTTCab applications, the user-side equipment is represented by ONU.
Internet connection methods: DSL VS Ethernet cable VS optical fiber
DSL, network cable and optical fiber are three common physical connection methods for accessing the Internet.
DSL is a broadband access technology that uses telephone lines as the transmission medium. DSL has many modes, including HDSL, SDSL, VDSL, ADSL, and RADSL, collectively referred to as xDSL. Ethernet cables are also called network cables. A network cable usually consists of 4 pairs of copper-core twisted pairs, using RJ45 connectors. Optical fibers are made of glass fibers and transmit data using the principle of total reflection of light.

So what are the differences between them?
- Material: DSL and Ethernet cables use copper cores, while optical fibers are made of glass.
- Transfer mode: DSL and Ethernet cables transmit signals in electrical pulses, while fiber optics transmit signals in light pulses.
- Transmission rate: DSL is generally less than 1 Mbps, but still some up to 100 Mbps. Ethernet cable download speed usually starts from 10Mbps to 500Mbps, and the upload speed is from 5Mbps to 50Mbps. The download and upload speed of a fiber patch cord can be anywhere from 250Mbps to 1000Mbps.
- Transmission distance: The DSL transmission distance does not exceed 5.5 kilometers (RASDL). The theoretical transmission distance of an Ethernet cable is 100 m. The transmission distance of single-mode fiber can reach 10-20 kilometers, and the transmission distance of multi-mode fiber can reach 2-3 kilometers, which is much higher than the transmission distance of Ethernet cables.
- Security: The optical fiber is made of quartz stone, which has good security and anti-interference, so the security of optical fiber is higher than that of DSL and Ethernet cables.
The above is an introduction to fiber optic networks. If you want to know more about fiber optic Internet, please contact us.




