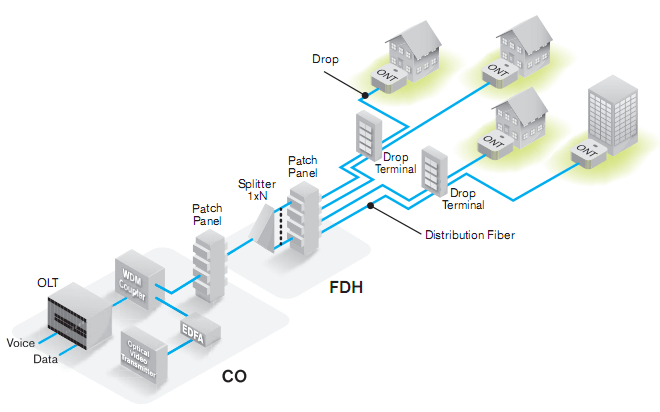
The FTTH network is divided into three parts: the central office OLT, the passive optical network (ODN), and the terminal (ONU). OLT accounts for a small proportion of single-user cost in the entire FTTH network construction. The utilization rate of the PON optical port is determined by the utilization rate of the optical splitter in the ODN network connected to it.
ODN is the part with the largest amount of engineering and the highest proportion of single-user cost in the entire fiber-to-the-home construction. The utilization rate of the optical splitter determines the utilization rate of the PON optical port; therefore, whether the ODN construction is reasonable not only affects its own cost but also affects the OLT cost.
When building an FTTH network, we should fully consider how to maximize the use of optical splitters in FTTH network construction. Here are some methods.
Maximize the use of splitters by splitting level
- Centralized splitting
Centralized splitting is suitable for high-rise residential buildings with a large number of users and basically stable living, or multi-story residential buildings with a large number of units. The number of users is equal to or slightly lower than an integer multiple of the splitter port (eg 1x 64). Optical splitters should be placed as concentrated as possible to facilitate deployment when individual ports are damaged. - Cascaded splitting
Cascade splitting is suitable for high-rise residential buildings with fewer users or multi-story residential buildings with fewer units. In order to improve port utilization, it is recommended to use the system stacking method of different PON ports to expand capacity instead of reserving ports. - Mixed use of concentrated splitting and cascade splitting
When a high-rise residential building or a multi-story residential building with a large number of units, the number of remaining users after centralized splitting is far less than an integer multiple of the first-level splitter (such as 1×64), the remaining users can use cascade splitting.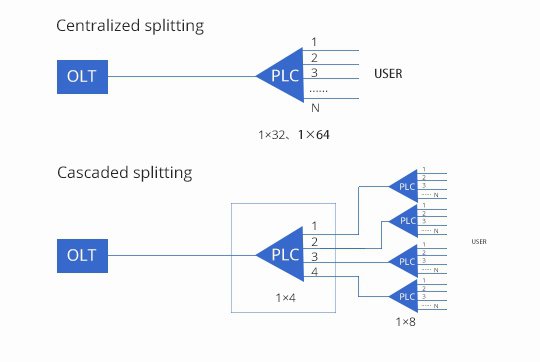
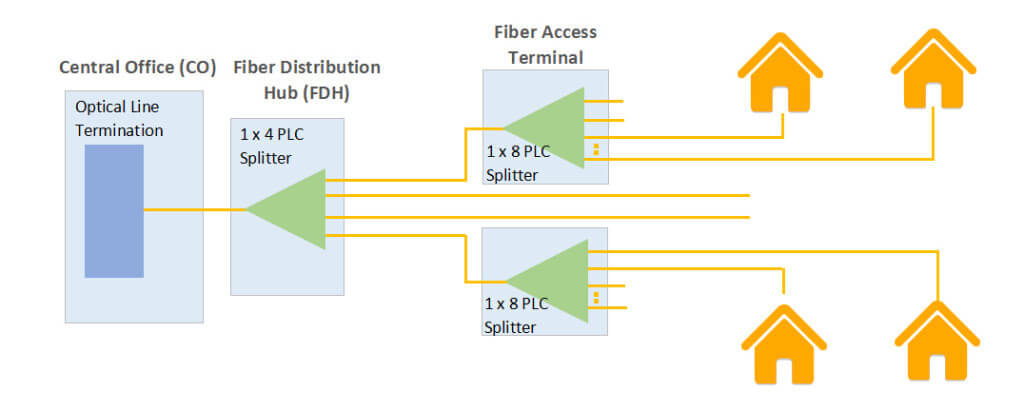
Maximize the use of splitters by the position of the first-level optical splitter (for cascaded splitting)
When adopting cascaded splitting, the position of the first-level optical splitter should be selected reasonably to cover as many residential buildings as possible. On the one hand, it can cover more residential buildings and avoid idle first-level splitter ports. On the other hand, when the OLT uses high-capacity PON ports, in order to facilitate network upgrades, the original concentrated splitting can be changed to cascade splitting by adding a light splitter, while for the original cascade splitting, the capacity can be increased by replacing the first-level splitter.
Maximize the use of splitters by residential density and user density
Residences are generally divided into high-end homes, villas, ordinary residential areas, urban villages, rural areas, etc. The specific characteristics are shown in the following.
| Residences | Characteristics |
| high-end homes, villas | residential density is low; access is relatively scattered |
| ordinary residential areas | high residential density; access is relatively concentrated |
| urban villages | high residential density; high turnover of people |
| rural areas | residential density is low; access is relatively scattered |
In the splitting level, centralized or cascaded optic splitting can be flexibly selected according to the residential density and user density.

High residential density does not mean high operator user density. The characteristic of fixed network access is that users cannot be developed without a network, and users cannot necessarily be developed with a network. Once the network is built, users cannot develop, and the return on investment is devastating. Therefore, network construction not only depends on residential density but also evaluates market capacity. It is particularly important to build a flexible network that is proportional to investment and income.
At the end
In the construction of the FTTH network, how to maximize the use of optical splitter, it is necessary to select a reasonable network coverage method according to the actual situation of the project, so as to improve ROI. Bonelinks improves various types of optical splitters, which can be widely used in FTTH network construction. Please contact us if you have any needs.