Fiber Optic Connectors are passive devices that implement active links between optical fibers. The common fiber cable connector types are LC, SC, MTP/MPO, ST, FC, and MTRJ. So, what’s the difference between them? Let’s learn more about different types of fiber connectors advantages and disadvantages.
LC vs SC vs FC vs ST vs MTP/MPO vs MTRJ Fiber Connectors: Different Structure
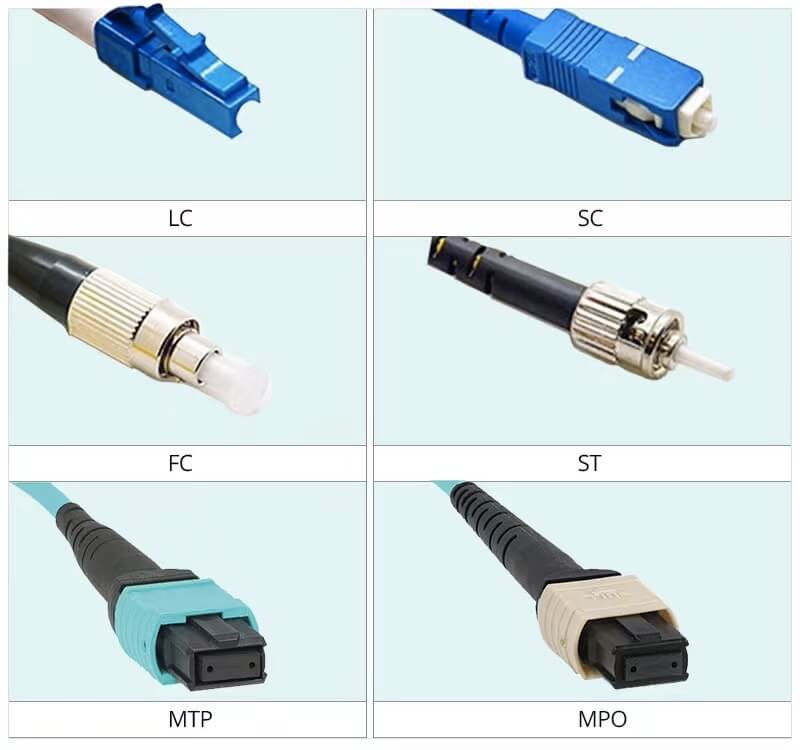
- LC connector adopts a push-pull locking structure, the shell is rectangular, made of plastic, and has a push button. Because the outer diameter of its ceramic pin is only 1.25mm, its external dimensions are also reduced accordingly, which greatly improves the density of the connector in the optical distribution frame. Normally, the LC connector is used in the form of a double-core connector, but it can also be separated into two single-core connectors if necessary. In addition, also a push-pull connector, the Lucent Connector LC utilizes a latch as opposed to the SC locking tab and with a smaller ferrule, it is known as a small form factor connector.
- SC connector adopts a plug-in structure, the outer shell is rectangular, and it is made of plastics. It is easy to make a multi-core connector. The straight body is a precision ceramic pin with an outer diameter of 2.5mm. A locking tab keeps this push-pull connector secure.
- FC connector adopts a metal thread connection structure, and the pin body adopts a precision ceramic pin with an outer diameter of 2.5mm. According to the shape of the pin end face, it is divided into FC/PC with spherical contact and FC/APC with oblique spherical contact. FC fiber optic connector was the first optical fiber connector to use a ceramic ferrule.
- ST connector adopts a bayonet locking structure with a key. The pin body is a precision ceramic pin with 2.5mm ferrule. The end face of the pin is usually a PC surface.
- The structure of the MPO/MPT connector is relatively complicated, and it connects 12 or 24 optical fibers in a rectangular optical fiber ferrule.
| Fiber Connector Types | Connection Type | Polishing Type |
| LC (lucent connector) | Latch | PC/APC/UPC |
| SC (Standard Connector, Subscriber Connector or Square Connector) | Push-pull | PC/APC/UPC |
| ST (Straight Tip) | Bayonet | PC/UPC |
| FC (Ferrule Connector) | Screw | PC/APC/UPC |
| MTP (Multi-fiber Termination Push-on) / MPO (Multi-fiber Push On) | Push-pull | APC/UPC |

LC vs SC vs FC vs ST vs MTP/MPO Fiber Connectors: Different Size
The size of the pins and sleeves used by the LC connector is the same as that used by ordinary SC and FC, which is 1.25mm, so its size is only half of that of SC/FC. The size of the FC fiber optic connector is the same as that of the SC connector.
| Fiber Connector Types | Diameter |
| LC | 1.25 mm |
| SC | 2.5 mm |
| ST | 2.5 mm |
| FC | 2.5 mm |
| MTP/MPO | 2.5 mm |
LC vs SC vs FC vs ST vs MTP/MPO Fiber Connectors: Different Application
- LC fiber optic connectors are manufactured with an easy-to-operate modular registered jack (RJ) latch mechanism, suitable for connection with SFP and SFP+ fiber optic transceivers.
- SC connectors are widely used in fiber optic user networks. It is usually used on the network equipment side to connect GBIC optical module. It is mostly used on router switches.
- ST connector is very convenient to use and is widely used in optical fiber user networks. It is usually used at the wiring equipment end, such as the optical fiber distribution frame, optical fiber module, etc. For 10Base-F connections, the connector is usually ST type. ST fiber optic connectors are suitable for long and short-distance applications, such as campus and building multimode fiber applications, enterprise network environments and military applications.
- FC connectors are widely used in fiber optic cable trunking systems, among which FC/APC connectors are used in occasions requiring high return loss, such as CATV networks, etc. It is generally used on the ODF side (the most used on the distribution frame). FC is mostly used in single mode, and is relatively rare in multimode fiber.
- MTP/MPO fiber optic connector is a special type of multi-fiber connector. It is usually used in high-density connection scenarios, such as data centers.
| Fiber Connector Types | Application |
| LC | both single-mode and multimode SFF (Small Form Factor) transceivers |
| SC | Gigabit Ethernet networks, datacom, and telecom applications |
| ST | both long and short distance applications such as campuses and building multimode fiber applications, corporate network environments, as well as military applications. |
| FC | datacom, telecom, measurement equipment, single-mode lasers, etc |
| MTP/MPO | high-speed data center and LAN applications |
LC vs SC vs FC vs ST vs MTP/MPO Fiber Connectors: Different Advantages and Disadvantages
- The size of the pin and sleeve used in the LC connector is half the size of ordinary SC, FC, etc., which is 1.25mm. This can increase the density of optical fiber connectors in the optical fiber distribution frame. The disadvantage of the Lucent Connector LC design is that SFF designs may be difficult to access in high-density fields.
- SC connectors are cheap, easy to plug and unplug, have small fluctuations in insertion loss, high compressive strength, high installation density, direct plug and pull, and are easy to use. The SC connector is made of engineering plastics, which have the advantages of high-temperature resistance and are not easy to oxidize. The disadvantage is that it is easy to fall out.
- ST connector is easy to plug and unplug, and has high compressive strength, and the disadvantage is that it is easy to break.
- FC connectors are metal connectors, and metal connectors can be plugged and unplugged more often than plastic connectors. This type of connector is simple in structure, easy to operate, reliable, and dust-proof. The disadvantage is that the installation time is slightly longer. The intricate design and use of metal make it more expensive.
- MPO/MTP connectors have the advantages of large cores count, small size, and high transmission rate, and are especially suitable for data centers with severe space constraints or a large number of optical fibers. However, MPO/MTP connector has a very sensitive surface that cannot be cleaned easily.
| Fiber Connector Types | Feature |
| LC | ease-operation, smaller size |
| SC | low price, easy push-pull operation, low insertion loss, good compression strength, |
| ST | easy to operate thanks to its spring-loaded design |
| FC | great for single-mode fibers and in an environment full of vibration |
| MTP/MPO | bend insensitive, carefully polished and low loss |
LC vs SC vs FC vs ST vs MTP/MPO Fiber Connectors: Different Typical Insertion Loss (db) and IEC Spec
| Fiber Connector Types | Typical Insertion Loss (DB) | IEC Spec |
| LC | 0.25 – 0.5 | 61754-20 |
| SC | 0.25 – 0.5 | 61754-4 |
| ST | 0.25 – 0.5 | 61754-2 |
| FC | 0.25 – 0.5 | 61754-13 |
| MTP/MPO | 0.25 – 0.75 | 61754-7 |
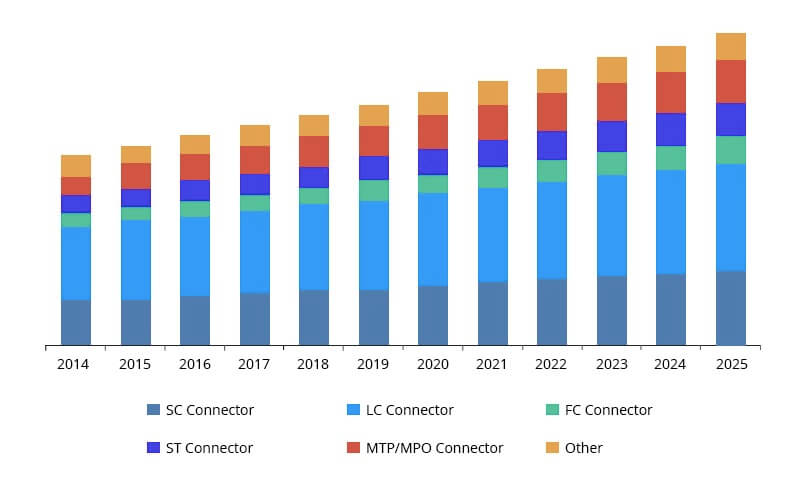
LC vs SC vs FC vs ST vs MTP/MPO Fiber Connectors: Different Market Share
The chart from Grand View Research shows the development of fiber optic connector types such as LC, SC, and MTP fiber optic connectors in recent years. It is easy to see from the chart that the growth of these 5 common fiber optic connectors is on a steady trend. Specifically, Lucent Connector LC connectors will continue to dominate the major optical connector market in the coming years, while the recent growth in demand for MTP/MPO connectors indicates that MTP/MPO connectors are likely to take more market share.
Summary
The above are the differences between FC, SC, LC and MTP/MPO connectors. Bonelinks provides standard Ceramic (Zirconia) ferrules with PC, UPC, APC, Conical and Step end-face for LC, SC, FC, ST, MTP/MPO fiber connectors and patch cord. Contact us if you have any requirements.




