Multi-core optical cables are widely used in high-density connections indoors and outdoors. Breakout cables and distribution cables are the commonly used multi-core optical cables. Then, what is the difference between breakout cable and distribution cable?
Breakout Cable VS Distribution Cable
Both breakout cable and distribution cable are composed of 900um tight buffered optical fiber. But they are different from each other, let us have a look at the main differences between them.
Structure
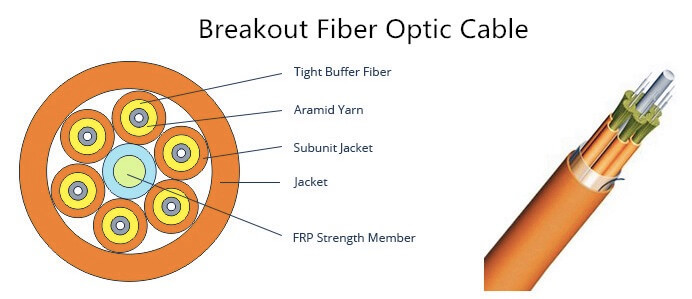
- Breakout cables (also known as fan-out cables) consist of two or more individual cables bundled together around a central strength member. Each fiber has its jacket, and all fibers are encapsulated in the same outer jacket. Therefore, when passing through the walls of buildings, breakout cables can also be split into individual simplex cables for separate use. The breakout optical cable is designed with φ900um tight buffer optical fiber, and the number of optical fibers varies from 2 to 24.
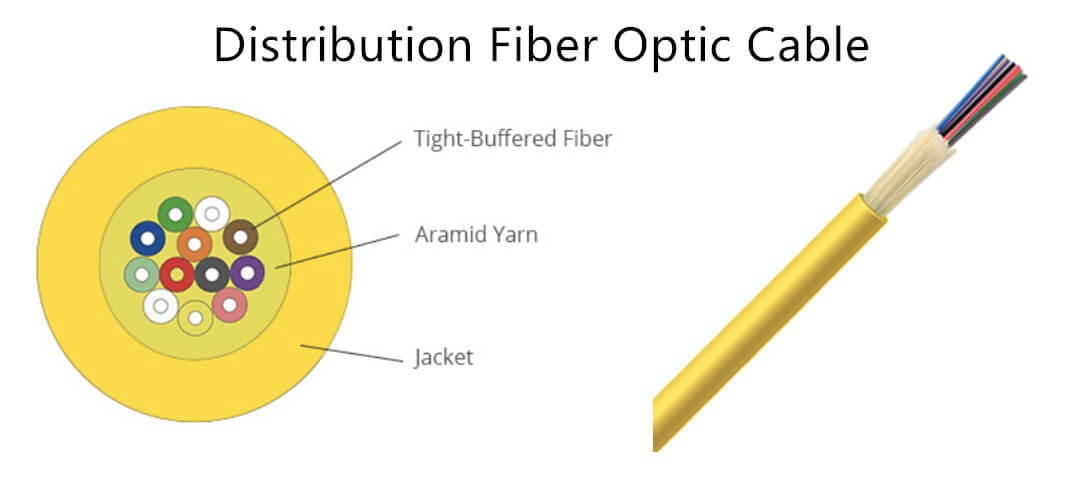
- Distribution optical cable uses φ900um tight-buffered optical fiber as the optical communication medium and aramid yarn reinforcement. The cables are sheathed in accordance with PVC or LSZH standards. Typically, distribution cables have a fiber count ranging from 2 to 144 fibers. According to different application requirements, the optical fiber cable is usually riser or plenum for flame-retardant, as well as unitary and non-unitized structures suitable for various environments.

Fiber type
- According to different fiber grades, breakout cables can be divided into breakout riser cables and breakout plenum cables. Breakout riser cables are widely used in vertical risers and general horizontal applications. But when fiber optic cables are required in ducts and other spaces with air return, breakout plenum fiber optic cables are the better choice.

- Distribution cables also come in riser and plenum cable types for indoor/outdoor applications. In addition to these types, distribution cables are sometimes equipped with an armored jacket for greater protection. Armored risers or plenum cables are available for harsh environments where heavy-duty protection is required.

Features and Benefits
- Breakout optical cables are light in weight and small in size. The outer protection material has the advantages of corrosion resistance, waterproof, UV protection, flame retardant, and environmental protection. Each fiber is individually strengthened, so it is also possible to divide the branch fiber optic cable into individual fiber optic lines. This enables fast connection of terminals and does not require a terminal block. Breakout optical cable has better economics, because it can save a lot of labor when connecting to the terminal, leaving room for damage or future expansion when connecting to the terminal.
- The distribution optical cable has excellent tight-buffered optical fiber stripping performance, and the aramid yarn strength member provides good tensile strength, small size, lighter weight, and more compact design. In addition, distribution fiber optic cables provide high-density connections, high reliability, easy preparation for termination, easy installation and maintenance, and low cost.
Application
- Breakout cables are widely used and are suitable for flame retardant, non-toxic, and non-smoke indoor applications. Breakout cables can also be used on framed or horizontal bridges. It’s ideal for local data centers, local area networks (LANs), indoors, backbones, levels, risers, plenums, conduits, junction boxes, patch panels and industrial applications.
- Distribution cables are suitable for indoor, indoor/outdoor applications, backbones within and between buildings, distribution frames, wiring between telecommunication rooms and connecting cables in risers and plenum environments, horizontal distribution for FTTD, data center EDA area and factory floor automation.
Breakout Cable VS Distribution Cable: How to Choose?
Both breakout cables and distribution cables are convenient solutions for multi-fiber applications. So how to choose? Here are some tips for reference.
- Compared with breakout optical cables, the distribution cable diameter is thinner with the same core counts, and it saves pipeline resources.
- Because breakout optical cable has an individual subunit jacket, it has advantages over maintenance, but the price is slightly more expensive than the distribution optical cable. When the cable is laid in the building, both distribution fiber optic cable and breakout fiber optic cable can be selected.
- It is recommended that distribution cables can be used for vertical cabling in the building, and breakout cables can be used for horizontal wiring.
In short, when purchasing breakout optical cables and distribution optical cables, you should choose according to your needs and fiber characteristics.